JEE Main Physics Question Paper with Solution 2022 July 25th Shift 1 - Morning
A
$\left[ P A ^{-1} T ^0\right]$
B
$\left[ P A T ^{-1}\right]$
C
$\left[ PA ^{-1} T \right]$
D
$\left[ P A ^{-1} T ^{-1}\right]$
Solution
Viscosity $=$ pascal.second
$ P ^{ x } A ^{ y } T ^{ z }=\left[ M ^1 L ^{-1} T ^{-1}\right] $
$ {\left[ M ^1 L ^{+1} T ^{-1}\right]^{ x }\left[ L ^2\right]^{ y }\left[ T ^1\right]^{ z }= M ^1 L ^{-1} T ^{-1}} $
$ M ^{ x } L ^{+ x +2 y } T ^{- x + z }= M ^1 L ^{-1} T ^{-1} $
$ x =1 \,\, x +2 y =-1 \,\,- x + z =-1 $
$ y =-1 $
$ z =0$
Viscosity $= P ^1 A ^{-1} T ^0$
A
Electric displacement $(\vec{D})$ and surface charge density
B
Displacement current and electric field
C
Current density and surface charge density
D
Electric potential and energy
Solution
Electric displacement
$ \vec{ D }=\epsilon_0 \vec{ E } $
$ {[ D ]=\left[\epsilon_0 E \right]=\left[\epsilon_0 \frac{\sigma}{\epsilon_0}\right]} $
$ {[ D ]=[\sigma]}$
$\rightarrow$ Surface change density $=\sigma$.
A
42 m
B
47 m
C
19 m
D
40 m
Solution
$ d = R \theta$
$ 60= R \left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}\right) $
$ R =\frac{60 \times 4}{3 \pi}=\frac{80}{\pi} m $
Displacement $=\sqrt{ R ^2+ R ^2-2 R ^2 \cos 135} $
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt{2 R ^2-2 R ^2(-0.7)}$
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt{3.4 R ^2}=\sqrt{3.4\left(\frac{80}{\pi}\right)^2}$
$\approx 47 m$
A
64 J
B
60 J
C
120 J
D
128 J
Solution
$v _{ i }=3\left(0^2\right)+4=4 \cong x =0$
$ v _{ F }=3(2)^2 \mid 4 \cong x =2$
$=16$
$ W =\Delta K =\frac{1}{2} m \left(16^2-4^2\right)$
$ =\frac{1}{2} \times \frac{1}{2}(256-16) $
$ =\frac{240}{4}=60 \,J $
A
$\sqrt{\frac{5}{3}}$
B
$\sqrt{\frac{4}{5}}$
C
$\sqrt{\frac{3}{5}}$
D
$\sqrt{\frac{14}{15}}$
Solution
$ V =\sqrt{\frac{2 gH }{1+ k ^2 / R ^2}}$
$ \frac{ V _{\text {cylinder }}}{ V _{\text {sphere }}}=\sqrt{\frac{\left(1+ k ^2 / R ^2\right)_{\text {sphere }}}{\left(1+ k ^2 / R ^2\right)_{\text {cylinder }}}} $
$ =\sqrt{\frac{1+2 / 5}{1+1 / 2}}=\sqrt{\frac{7}{5} \times \frac{2}{3}}=\sqrt{\frac{14}{15}}$
A
21 G
B
100 G
C
59 G
D
42 G
Solution

$ F =\frac{ GMM }{ r ^2}+\sqrt{2} \frac{ GMM }{(\sqrt{2} r )^2}$
$ =\frac{ GMM }{ r ^2}\left(1+\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right) $
$ =\frac{ G \times 10^4}{13^2}\left(1+\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right) $
$ F \simeq 100 G $
A
$3.536 \times 10^5 Pa$
B
$3.536 \times 10^6 Pa$
C
$1.25 \times 10^6 Pa$
D
$1.25 \times 10^5 Pa$
Solution
$ P _1=2 \times 10^7 Pa $
$P _1 V _1= P _2 V _2$
Since $V_2=2 V_1$ Hence $P_2=P_1 / 2$ (isothermal expansion)
$ P_2=1 \times 10^7 Pa $
$ P_2\left(V_2\right)^\gamma=P_3\left(2 V_2\right)^\gamma$
$P_3=\frac{1 \times 10^7}{2^{1.5}}=3.536 \times 10^6$
A
(1) and (4) only
B
(1), (2) and (4) only
C
(2) and (4) only
D
(1), (2) and (5) only
Solution
$ KE _{\text {avg }}=\frac{3}{2} KT$
$P =\frac{1}{3} \rho V _{ rms }^2$
Note : Statement (4) is correct only if we consider it at constant volume and not constant pressure. Ideally, this question must be bonus but most appropriate answer is option (A)
A
$\frac{T_1}{T_2}=\frac{3}{\sqrt{2}}$
B
$\frac{T_1}{T_2}=\sqrt{\frac{3}{2}}$
C
$\frac{ T _1}{ T _2}=\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}$
D
$\frac{ T _1}{ T _2}=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{3}$
Solution
$ T _1=2 \pi \sqrt{\frac{3 m }{2 k }}$
$ T _2=2 \pi \sqrt{\frac{ m }{3 k }} $
$ \frac{ T _1}{ T _2}=\frac{2 \pi \sqrt{\frac{3 m }{2 k }}}{2 \pi \sqrt{\frac{ m }{3 k }}}=\frac{3}{\sqrt{2}}$
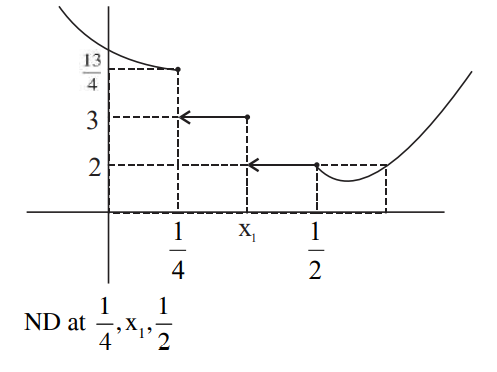
A
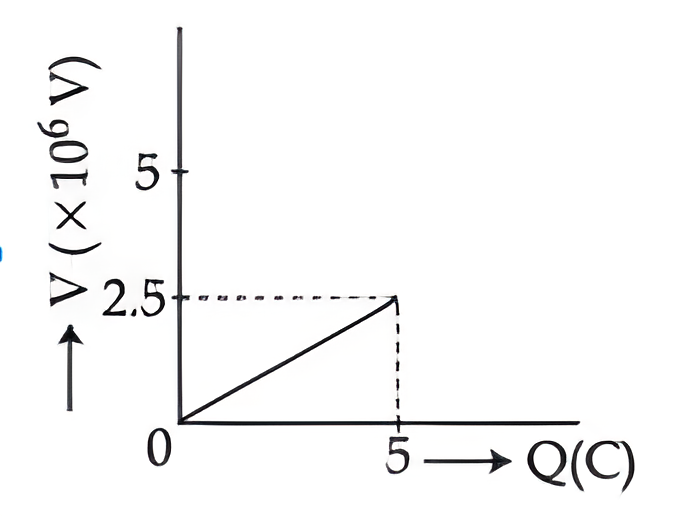
B
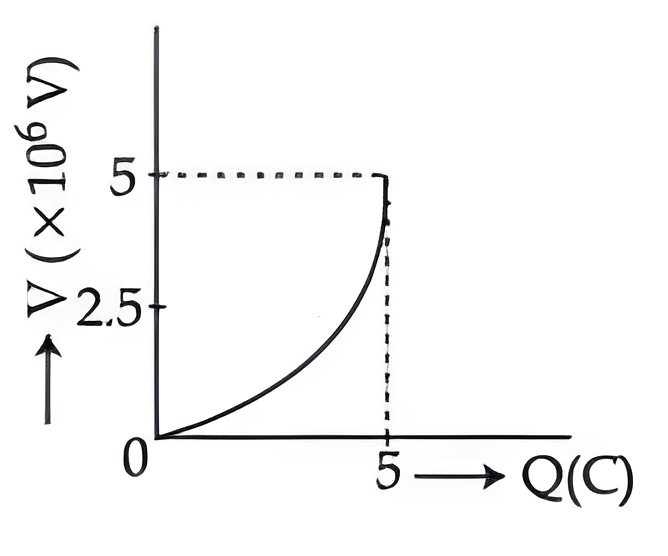
C
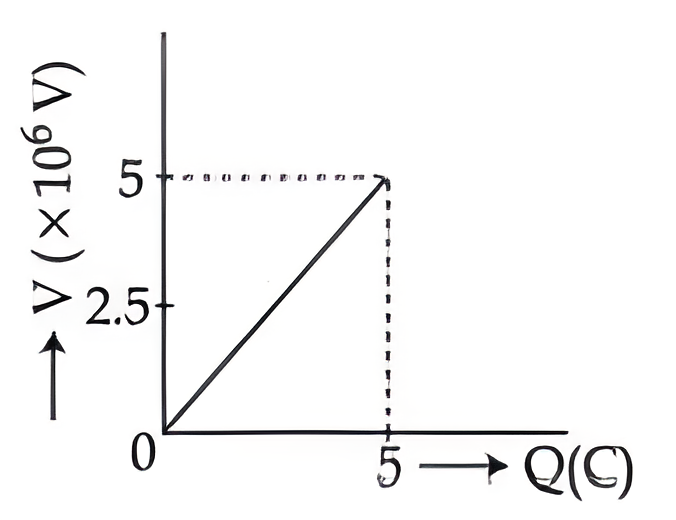
D
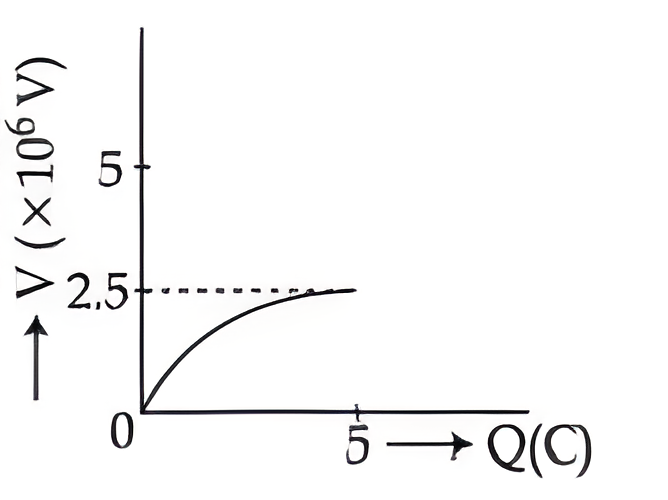
Solution
$ Q = CV$
$V =\frac{1}{ C } Q$
Straight line with slope $=\frac{1}{ C }$
Slope $=\frac{1}{C}=\frac{1}{2 \times 10^{-6}}=5 \times 10^5$
A
$8: 5$
B
$5: 4$
C
$5: 3$
D
$8: 7$
Solution
Radius of circular path $R =\frac{\sqrt{2 mk }}{ qB }$
$ q =\frac{\sqrt{2 mk }}{ RB } $
$ \frac{ q _1}{ q _2}=\sqrt{\frac{ m _1}{ m _2}} \times \frac{ R _2}{ R _1}=\sqrt{\frac{9}{4}} \times \frac{5}{6}=\frac{5}{4}$
A
Source frequency should be increased
B
Another resistance should be added in series with the first resistance.
C
Another capacitor should be added in series with the first capacitor
D
The source frequency should be decreased
Solution
$f=\frac{1}{2 \pi \sqrt{L C}}$
To increase the resonating frequency product of $L$ and $C$ should decrease.
By joining capacitor in series, capacitor will decrease
A
$\frac{2 \sqrt{2} \mu_0 L ^2}{\pi \ell}$
B
$\frac{\mu_0 \ell^2}{2 \sqrt{2} \pi L }$
C
$\frac{2 \sqrt{2} \mu_0 \ell^2}{\pi L }$
D
$\frac{\mu_0 L^2}{2 \sqrt{2} \pi \ell}$
Solution
Assuming current I in outer loop magnetic field at centre $=4 \times \frac{\mu_0 i }{4 \pi \times \frac{ L }{2}} \times\left(2 \sin 45^{\circ}\right)=\frac{2 \sqrt{2} \mu_0 i }{\pi L }$

$ M=\frac{\text { Flux through inner loop }}{ i } $
$ M =\frac{2 \sqrt{2} \mu_0 \ell^2}{\pi L }$
A
$5 \, pF$
B
$50 \, pF$
C
$100 \, pF$
D
$200\, pF$
Solution
Current in capacitor $I =\frac{ V }{ X _{ C }}$
$ I =( V ) \times(\omega C )$
$ C =\frac{ I }{ V \omega}=\frac{6.9 \times 10^{-6}}{230 \times 600}=50 \,pF$
A
In primary rainbow, observer sees red colour on the top and violet on the bottom
B
In primary rainbow, observer sees violet colour on the top and red on the bottom
C
In primary rainbow, light wave suffers total internal reflection twice before coming out of water drops
D
Primary rainbow is less bright than secondary rainbow.
Solution
In primary rainbow, red colour is at top and violet is at bottom.
Intensity of secondary rainbow is less in comparison to primary rainbow.
A
$5 \times 10^{-10} v _{ a } m$
B
$5 \times 10^{-10} m$
C
$1.5 \times 10^{-10} m$
D
$5 \times 10^{-10} v _{ B } m$
Solution
$\frac{\mu_{ A }}{\mu_{ B }}=\frac{ c / V _{ A }}{ c / V _{ B }}=\frac{ V _{ B }}{ V _{ A }}=\frac{1}{2}$
Let the thickness is $d$
$\frac{ d }{ v _{ B }}-\frac{ d }{ v _{ A }}=5 \times 10^{-10} $
$d =\frac{5 \times 10^{-10} \times v _{ A } v _{ B }}{ v _{ A }- v _{ B }}$
As $v _{ A }=2 v _{ B } \Rightarrow d =5 \times 10^{-10} \times 2 v _{ B }$
Or $d =5 \times 10^{-10} \times v _{ A }$
A
$1.537 \,eV$
B
$2.46 \,eV$
C
$0.615\, eV$
D
$1.23 \,eV$
Solution
$ k _1=\frac{1230}{800}-\phi..... $(1)
$ k _2=2 k _1=\frac{1230}{500}-\phi.....$(2)
Eliminating $k _1$ from (1) and (2) we get
$ 0=\frac{1230}{500}-\frac{1230}{400}+\phi$
$ \phi=0.615 \,eV$
A
$\frac{ nh }{2 \pi r }$
B
$\frac{ nh }{2 r }$
C
$\frac{n h}{2 \pi}$
D
$\frac{2 \pi r }{ nh }$
Solution
Angular momentum is integral multiple of $\frac{ h }{2 \pi} mvr =\frac{ nh }{2 \pi}$
So momentum mv $=\frac{ nh }{2 \pi r }$
A
$\vec{\mu}_{ L }=\frac{ e \overrightarrow{ L }}{2 m }$
B
$\vec{\mu}_{ L }=-\frac{e \overrightarrow{ L }}{2 m }$
C
$\vec{\mu}_1=-\frac{e \vec{L}}{m}$
D
$\vec{\mu}_1=\frac{2 e \vec{L}}{m}$
Solution
Ratio of magnetic moment and angular momentum
$\frac{\vec{\mu}}{\overrightarrow{ L }}=\frac{ q }{2 m }$
For $^{-}$
$\vec{\mu}=-\frac{ e }{2 m } \overrightarrow{ L }$
A
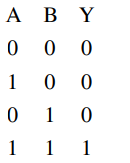
B
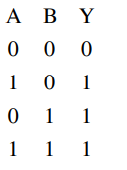
C
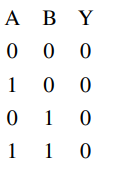
D
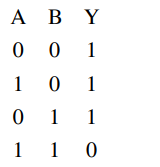
Solution
When both $A$ and $B$ have logical value ' $1$ '
both diode are reverse bias and current will flow in resistor hence output will be $5$ volt i.e. logical value ' $1$ '.
In all other case conduction will take place, hence output will be zero volt i.e. logical value ' $0$ '.
So truth table is
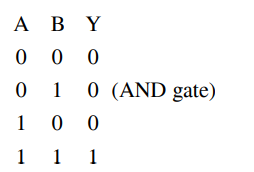
Answer: 3
Solution
Stopping distance $=\frac{ v ^2}{2 a }= d$
If speed is made $\frac{1}{3} rd$
$d ^{\prime}=\frac{1}{9} d . \,\,d ^{\prime}=\frac{27}{9}=3$
Braking acceleration remains same
Answer: 3
Solution

$\theta=45^{\circ}$
Taking components along $x$ & $y$
$ F _1=\sqrt{2}-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{2-1}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$
$ F _2=\sqrt{2}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{2+1}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{3}{\sqrt{2}}$
$F _1: F _2=1: 3 $
$ x =3$
Answer: 5
Solution
$ \Delta \ell_1=\frac{ F \ell}{ AY }=\frac{ F \ell}{\pi r ^2 Y }=5\, cm$
$ \Delta \ell_2=\frac{4 F 4 \ell}{\pi 16 r ^2 Y }=\frac{ F \ell}{\pi r ^2 Y }=5 \,cm $
Answer: 60
Solution
$ \ell_{ B }\left(1+\alpha_{ B } \Delta T \right)-\ell_{ i }\left(1+\alpha_{ i } \Delta T \right)=\ell_{ B }-\ell_{ i }$
$ \alpha_{ B } \ell_{ B }=\ell_{ i } \alpha_{ i } $
$ 1.8 \times 10^{-5} \times 40=\ell_{ i } \times 1.2 \times 10^{-5}$
$\ell_{ i }=\frac{1.8 \times 10^{-5} \times 40}{1.2 \times 10^{-5}}=\frac{3 \times 40}{2}=60 $
$ \ell_{ i }=60\, cm$
Answer: 20
Solution

$V_S=0, V_{\text {ob }}=5\, m / s$
$ f _{\text {direct }}=\left(\frac{320-5}{320}\right) 640=630\, Hz$
$ f _{\text {reflected }}=\left(\frac{320+5}{320}\right) 640=650\, Hz $
$ f _{\text {beat }}=650-630=20\, Hz $
Answer: 45
Solution
No. of electric field lines per unit area $=$ electric field.
$E =\frac{\rho r }{3 \in_0}$, for $r = R$
$E =\frac{\rho R }{3 \epsilon_0}=\frac{2 \times 6}{3 \times 8.85 \times 10^{-12}}=0.45 \times 10^{12} NC ^{-1}$
$=45 \times 10^{10} N / C$
Answer: 4
Solution

By nodal analysis
$ \frac{ V _0-2}{1 k \Omega}+\frac{ V _0-4}{1 k \Omega}+\frac{ V _0-6}{1 k \Omega}=0$
$ 3 V _0-12=0 $
$ V _0=4$
Answer: 4
Solution
Each wire has resistance $=\rho \frac{4 \ell}{\pi d ^2}= r$
Eight wire in parallel, then equivalent resistance is $\frac{ r }{8}=\frac{\rho \ell}{2 \pi d ^2}$
Single copper wire of length $2 l$ has resistance
$ R =\rho \frac{2 \ell \times 4}{\pi d _1^2}=\frac{\rho \ell}{2 \pi d ^2}$
$ \Rightarrow d _1=4 d$
Answer: 3
Solution
$E _{ g }=\frac{ hc }{\lambda}=\frac{1242}{\lambda( nm )}=\frac{1242}{400}=3.105$
Answer rounded to $3\, eV$
Answer: 150
Solution
$ d =\sqrt{2 Rh } $
$ d =\sqrt{2 \times 6400 \times h \times 10^{-3}}( h$ in $m )$
Area $=\pi d ^2 $
$ =\left(\pi \times 2 \times 6400 \times h \times 10^{-3}\right) km ^2 $
$ 6.03 \times 100000=100 \times \pi \times 2 \times 6400 \times 10^{-3} h $
$ h =\frac{6.03 \times 10^5}{10 \times \pi \times 128} $
$ h =150 \,m$
JEE Main Chemistry Question Paper with Solution 2022 July 25th Shift 1 - Morning
A
16
B
8
C
4
D
2
Solution
Let $n \left( SO _2 Cl _2\right)= x$ moles
$ \therefore n \left( H _2 SO _4\right)= x , n ( HCl )=2 x$
$\Rightarrow n \left( H ^{+}\right)=4 x $
For Neutralisation
$ \Rightarrow n \left( H ^{+}\right)= n \left( OH ^{-}\right) $
$\Rightarrow 4 x =16$
$\Rightarrow x =4$
A
$n =3,1=2, m _{ l }=0, s =+\frac{1}{2}$
B
$n =3,1=2, m _1=-2, s =+\frac{1}{2}$
C
$n =3,1=3, m _{ l }=-3, s =-\frac{1}{2}$
D
$n =3,1=0, m _1=0, s =-\frac{1}{2}$
Solution
$ 1=0,1,2 \ldots \ldots(n-1) $
$\therefore \text { for } n =3 $
$1=0,1,2$
$ \Rightarrow 1=3 $
not possible for $n =3$
A
$0.8$
B
$1.1$
C
$1.9$
D
$2.4$
Solution
${[ HCOOH ]=0.5 \,ml ^{-1}} $
$ \Rightarrow\left(0.5\, ml \times 1.05 \,g \,ml ^{-1}\right) HCOOH \text { in } 1 L $
$ \Rightarrow 0.525 \,g \,HCOOH$ in $1 L $
$ m =\frac{(0.525 / 46)}{1 \,kg } mol$
[Assuming dilute solution]
$\therefore \Delta T _{ f }= iK _{ f } m \Rightarrow i =\frac{\Delta T _{ f }}{ k _{ f } m }=\frac{0.0405 \times 46}{1.86 \times 0.525}=1.9$
A
$3.2$
B
$4.2$
C
$5.2$
D
$6.2$
Solution

$pH =\frac{ pK _{ w }- pK _{ b }-\log C }{2}$
$=\frac{14-5+1.48}{2}=5.24$
A
(A) - (II), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (III)
B
(A) - (II), (B) - (I), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III)
C
(A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (II)
D
(A) - (III), (B) - (I), (C) - (IV), (D) - (II)
Solution
Factual
A
Unnilbium
B
Unnilunium
C
Unnilquadium
D
Unniltrium
Solution
Atomic Number 103
A
(3) (4) Only
B
(1), (2), (5) Only
C
(1), (2) Only
D
(2) Only
Solution
$FeO + SiO _2 \rightarrow FeSiO _3$
A
$Mn ^{2+}$
B
$Mn ^{4+}$
C
$Mn ^{3+}$
D
$Mn ^{6+}$
Solution
$H _2 O _2+ MnO _4^{-} \rightarrow Mn ^{2+}+ O _2$ (unbalanced $)$
A
$Li < K < Na < Rb < Cs$
B
$Li < Na < K < Rb < Cs$
C
$Cs < Rb < K < Na < Li$
D
$Li < Na < K < Cs < Rb$
Solution
Factual
A
trigonal planar
B
tetrahedral
C
pyramidal
D
square planar
Solution
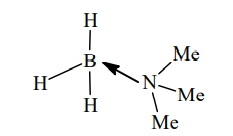
$BF_3 + NaH \xrightarrow{450\,K} \underset{\text{(diborane)}}{B_2H_6} + NaF$
$B_2H_6 + NMe_3 \rightarrow \underset{\text{symmetrical cleavage}}{2[BH_3 \leftarrow NMe_3]}$
A
hypohalite
B
halate
C
perhalate
D
halite
Solution
$Br_2 + \underset{\text{(excess)}}{ 5F_2} \rightarrow \overset{+5}{2BrF_5} \xrightarrow{H_2O} HBrO_3$ (Forms bromate)
A
$NO$
B
$NO _2$
C
$SO _2$
D
$HCHO$
Solution
Factual
A
$KMnO _4 / H ^{+}$and dil. $KMnO _4, 273 \,K$
B
$KMnO _4$, (dilute), $273 K$ and $KMnO _4 / H ^{+}$
C
$KMnO _4 / H ^{+}$and $O _3, H _2 O / Zn$
D
$O _3, H _2 O / Zn$ and $KMnO _4 / H ^{+}$
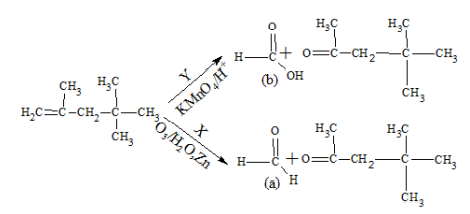
A
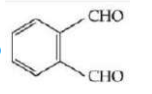
B
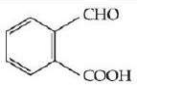
C
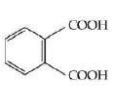
D
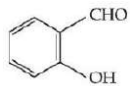
Solution
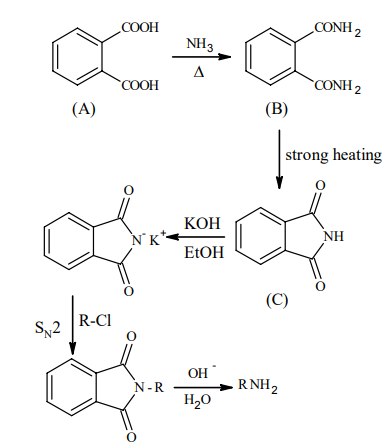
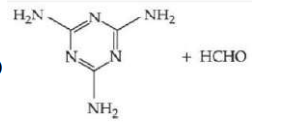
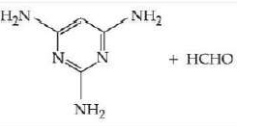
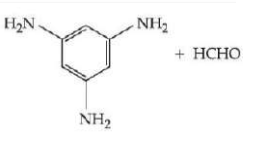
Gabriel Pthalimide reaction
A
B
C
D
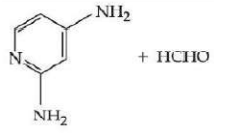
Solution

Formaldehyde $HCHO$
Melamine formaldehyde Resin is melamine polymer
A
Primary
B
Secondary
C
Tertiary
D
Quaternary
Solution
Primary structure remains intact during denaturation of proteins
A
Agonists
B
Antagonists
C
Allosterists
D
Anti histaminists
Solution
Factual
A
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
B
Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
C
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
D
Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
Solution
Acrolein has a pungent, suffocating odour. Acrolein is used to detect presence of glycerol
Answer: 2
Solution
Diamagnetic species are: $N _2, O _2^{2-}$
Answer: 104
Solution
$ 3 C _{( gr )}+4 H _{2( g )} \rightarrow C _3 H _{8( g )} $
$ =-103.7 \,kJ\, mol ^{-1}$
Answer: 22
Solution
$ {\left[ P _{ gas }\right]_0+\text { V.P. }=4}$
$ {\left[ P _{ gas }\right]_0=4-0.4=3.6}$
As volume is doubled, $\left[ P _{ gas }\right]_{\text {new }}=1.8\, atm$
New Total Pressure $=1.8+0.4=2.2 a\,tm$
Answer: 4
Solution
$ E = E ^0-\frac{2.303 RT }{ nF } \log Q$
Here, $ E =+0.801 \,V , E ^0=0.008-(-0.763) $
$=+0.771\, V $
$ \therefore 0.801=+0.771-\frac{0.06}{ n } \log 10^{-2} $
$ \Rightarrow n =4$
Answer: 1
Solution
$\left( t _{1 / 2}\right)_{500 \text { torr }}=240 \,\sec =4\,\min$.
$\left( t _{1 / 2}\right)_{250 \text { torr }}=4 \,\min$.
$t _{1 / 2} \propto a ^{1- n }$
As $t_{1 / 2}$ is independent of initial pressure. Hence, order is $1 st$ order.
Answer: 0
Solution
$\Delta_0 \propto \frac{1}{\lambda}$
Here, $CN ^{-}$being SFL will have maximum CFSE
So, $\left[ Co ( CN )_6\right]^{3-}$ will be $d ^2 sp ^3, \mu=0$
Answer: 5
Solution
$Co ^{3+}$ can't liberate $H _2$.
It has $d ^6$ configuration,
Number of unpaired electrons $=4$
$\mu=\sqrt{4 \times 6}=4.92 \text { B.M. }$
Answer: 56
Solution
$ \% N =\frac{1.4\left( N _1 V _1\right)}{\text { massof organic compound }} $
$ \% N =\frac{1.4(2.5 \times 2 \times 2)}{0.25}=56$
JEE Main Mathematics Question Paper with Solution 2022 July 25th Shift 1 - Morning
A
60
B
90
C
108
D
126
Solution
$ A =\{1,2,3,4\} $
$ B =\{1,2,3,4,5,6\}$
Here $f(3)$ can be $2,3,4,5,6$
$f (3)=2,( f (1), f (2)) \rightarrow(1,1) \rightarrow 6 $ cases
$ f (3)=3,( f (1), f (2)) \rightarrow(1,2),(2,1) $
$ \rightarrow 2 \times 6=12 $ cases
$ f (3)=4,( f (1), f (2)) \rightarrow(1,3),(3,1),(2,2)$
$\rightarrow 3 \times 6=18 $ cases
$ f (3)=5,( f (1), f (2)) \rightarrow(1,4),(4,1),(2,3)$
$ (3,2) $
$ \rightarrow 4 \times 6=24 $ cases
$ f (3)=6, ( f (1), f (2))$
$ (1,5),(5,1),(2,4),(4,2),(3,3)$
$ \rightarrow 5 \times 6=30 $ cases
Total number of cases $=6+12+18+24+ 30=90$
A
$-4$
B
$-1$
C
1
D
4
Solution
$\alpha, \beta, \gamma, \delta$ root of the equation
$x^4+x^3+x^2+x+1=0$
Which are $5^{\text {th }}$ roots of unity except 1 . then $\alpha^{2021}+\beta^{2021}+\gamma^{2021}+\delta^{2021}=$ $\alpha+\beta+\gamma+\delta=-1$
A
0
B
2
C
3
D
4
Solution
$S_n:|z-(3-2 i)|=\frac{n}{4}$ is a circle center $C _1(3,-2)$ and radius $n / 4$
$T _{ n }:| z -(2-3 i )|=\frac{1}{ n }$ is a circle center $C _2$ $(2,-3)$
and radius $1 / n$
Here $S_n \cap T_n=\phi$
Both circles do not intersect each other
Case-1 : $C _1 C _2> n / 4+1 / n$
$\sqrt{2}>\frac{ n }{4}+\frac{1}{ n }$
then $n =1,2,3,4$
Case-2 : $C _1 C _2<\left|\frac{ n }{4}-\frac{1}{ n }\right|$
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{2} < \left|\frac{n^2-4}{4 n}\right|$
$\Rightarrow n$ has infinite solutions for $n \in N$
A
6
B
7
C
8
D
9
Solution
The system of equation has no solution.
$ D = \begin{vmatrix}3 \sin 3 \theta & -1 & 1 \\3 \cos 2 \theta & 4 & 3 \\6 & 7 & 7\end{vmatrix}=0 $
$ 21 \sin 3 \theta+42 \cos 2 \theta-42=0$
$ \sin 3 \theta+2 \cos 2 \theta-2=0$
Number of solution is 7 in $(0,4 \pi)$
A
4
B
$-8$
C
$-4$
D
8
Solution
$ \displaystyle\lim _{n \rightarrow \infty} n\left(1-\frac{n+1}{n^2}\right)^{\frac{1}{2}}+\alpha n+\beta=0$
$ \displaystyle\lim _{n \rightarrow \infty}\left\{11-\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{n+1}{n^2}\right)+\frac{\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)}{2 !}\left(\frac{n+1}{n^2}\right)^2+\ldots .\right\}+\alpha n+\beta=0 $
$ \displaystyle\lim _{n \rightarrow \infty} n-\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{n}+\ldots .+n \alpha+\beta=0$
$ \alpha=-1, \beta=\frac{1}{2}$
$ 8(\alpha+\beta)=-4$
A
$\alpha=0$
B
$\alpha=-3$
C
$\alpha \in(-1,0)$
D
$\alpha \in(-3,-1)$
Solution
$ f ^{\prime}( x )= e ^{\left(4 x ^3-12 x ^2-180 x +31\right)}\left(12\left( x ^2-2 x +7\right)( x +3)( x -5)+2( x -1)\right)$
$ \text { for } x \in[-3,0] $
$\Rightarrow f ^{\prime}( x ) < 0$
$f(x) $ is decreasing function on $ [-3, 0]$
The absolute maximum value of the function $f(x)$ is at $x=-3$
$\Rightarrow \alpha=-3$
A
$\frac{27}{4}$
B
$\frac{29}{4}$
C
$\frac{37}{4}$
D
$\frac{9}{2}$
Solution
$y(x)=a x^3+b x^2+c x+5$ is passing through $(-2,0)$ then $8 a-4 b+2 c=5 \ldots \ldots$ (1)
$y^{\prime}(x)=3 a x^2+2 b x+c$ touches $x$-axis at $(- 2,0)$
$12 a-4 b+c=0 .....$(2)
again, for $x=0, y^{\prime}(x)=3$
$c =3 .....$(3)
Solving eq. (1), (2) \& (3) $a =-\frac{1}{2}, b =-\frac{3}{4}$
$y^{\prime}(x)=-\frac{3}{2} x^2-\frac{3}{2} x+3$
$y(x)$ has local maxima at $x=1$
$y(1)=\frac{27}{4}$
A
$\frac{31}{8}$
B
$\frac{17}{6}$
C
$\frac{19}{6}$
D
$\frac{27}{8}$
Solution

$A=\int\limits_{-1}^{\frac{1}{2}}\left(x+2-x^2\right) d x+\int\limits_{\frac{1}{2}}^1\left(4-3 x-x^2\right) d x=\frac{17}{6}$
A
4
B
2
C
1
D
0
Solution
$f(x)$ is periodic function whose period is 2
$ \frac{\pi^2}{10} \int\limits_{-10}^{10} f(x) \cos \pi x d x=\frac{\bar{\pi}^2}{10} \times 10 \int\limits_0^2 f(x) \cos \pi x d x $
$ =\pi^2\left(\int\limits_0^1(1-x) \cos \pi x d x+\int\limits_1^2(x-1) \cos \pi x d x\right)$
Using by parts
$=\pi^2 \times \frac{4}{\pi^2}=4$
A
$\frac{3+\sqrt{2}}{3-\sqrt{2}}$
B
$\frac{3}{\sqrt{2}}\left(\frac{3+\sqrt{2}}{3-\sqrt{2}}\right)$
C
$\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\left(\frac{\sqrt{2}+1}{\sqrt{2}-1}\right)$
D
$\frac{\sqrt{2}+1}{\sqrt{2}-1}$
Solution
$ \frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{2 e^{2 x}-6 e^{-x}+9}{2+9 e^{-2 x}} $
$ \frac{d y}{d x}=e^{2 x}-\frac{6 e^x}{2 e^{2 x}+9} $
$ y=\frac{e^{2 x}}{2}-\tan ^{-1}\left(\frac{\sqrt{2} e^x}{3}\right)+c$
If $C$ passes through the point $\left(0, \frac{1}{2}+\frac{\pi}{2 \sqrt{2}}\right)$
$c=-\frac{\pi}{4}-\tan ^{-1} \frac{\sqrt{2}}{3}$
Again C passes through the point $\left(\alpha, \frac{1}{2} e ^{2 \alpha}\right)$
then $e ^\alpha=\frac{3}{\sqrt{2}}\left(\frac{3+\sqrt{2}}{3-\sqrt{2}}\right)$
A
$\left(y^2+x\right)^4=C\left|\left(y^2+2 x\right)^3\right|$
B
$\left( y ^2+2 x \right)^4= C \left|\left( y ^2+ x \right)^3\right|$
C
$\left|\left(y^2+x\right)^3\right|=C\left(2 y^2+x\right)^4$
D
$\left|\left(y^2+2 x\right)^3\right|=C\left(2 y^2+x\right)^4$
Solution
$ \left(x-y^2\right) d x+y\left(5 x+y^2\right) d y=0$
$ \frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{y^2-x}{y\left(5 x+y^2\right)} . \text { Let } y^2=v $
$\frac{2 y d y}{d x}=2\left(\frac{y^2-x}{5 x+y^2}\right) $
$ \frac{d v}{d x}=2\left(\frac{v-x}{5 x+v}\right) v=k x$
$ k + x \frac{ dk }{ dx }=2\left(\frac{ kx - x }{5 x + kx }\right) $
$x \frac{ dk }{ dx }=-\frac{\left( k ^2+3 k +2\right)}{ k +5}$
$\int \frac{(5+k)}{(k+1)(k+2)} d k=\int-\frac{d x}{x}$
$ \int\left(\frac{4}{k+1}-\frac{3}{k+2}\right) d k=-\int \frac{d x}{x}$
$ 4 \ln (k+1)-3 \ln (k+2)=-\ln x+\ln c $
$ \frac{(k+1)^4}{(k+2)^3}=-\ln x+\ln c $
$ c\left(y^2+2 x\right)^3=\left(y^2+x\right)^4$
A
$2 x+y=9$
B
$3 x-2 y=7$
C
$x+2 y=6$
D
$2 x -3 y =3$
Solution
Let $B\left(x_1, x_1-2\right)$
$\sqrt{\left(x_1-4\right)^2+\left(x_1-2-3\right)^2}=\frac{\sqrt{29}}{3}$
Squaring on both side $18 x _1^2-162 x _1+340=0$
$x _1=\frac{51}{9} $ or $ x _1=\frac{10}{3}$
$y _1=\frac{33}{9} $ or $ y _1=\frac{4}{3}$
Option (C) will satisfy $\left(\frac{10}{3}, \frac{4}{3}\right)$
A
$\frac{32 \sqrt{2}}{3}$
B
$\frac{40 \sqrt{2}}{3}$
C
$\frac{64}{3}$
D
$\frac{32}{3}$
Solution
$ (\alpha-0)^2+(\beta-1)^2=(\beta+1)^2$
$\alpha^2=4 \beta $
$ x^2=4 y$
$ A=2 \int\limits_0^4\left(4-\frac{x^2}{4}\right) d x=\frac{64}{3}$
A
$\frac{147}{2}$
B
96
C
$\frac{32}{3}$
D
54
Solution
$a ( x -3)+ b ( y +4)+ c ( z -7)=0$
$ P : 9 a - b -5 c =0$
$ -11 a - b +5 c =0$
After solving DR's $\propto(1,-1,2)$
Equation of plane
$x - y +2 z =21 $
$ d =\frac{8}{\sqrt{6}} $
$ d ^2=\frac{32}{3}$
A
both (S1) and (S2) are true
B
only (S1) is true
C
only (S2) is true
D
both (S1) and (S2) are false
Solution
$ \overrightarrow{ a }+\overrightarrow{ b }+\overrightarrow{ c }=0 $
$\overrightarrow{ b }+\overrightarrow{ c }=-\overrightarrow{ a }$
$|\overrightarrow{ b }|^2+|\overrightarrow{ c }|^2+2 \overrightarrow{ b } \cdot \overrightarrow{ c }=|\overrightarrow{ a }|^2 $
$ |\overrightarrow{ c }|^2=36$
$ |\overrightarrow{ c }|^2=6$
$ S1: |\vec{a} \times \vec{b}+\overrightarrow{ c } \times \overrightarrow{ b }|-|\overrightarrow{ c }| $
$ |(\overrightarrow{ a }+\overrightarrow{ c }) \times \overrightarrow{ b }|-|\overrightarrow{ c }|$
$ |-\overrightarrow{ b } \times \overrightarrow{ b }|-|\overrightarrow{ c }| $
$ 0-6=-6$
$ S 2: \overrightarrow{ a }+\overrightarrow{ b }+\overrightarrow{ c }=0$
$ \overrightarrow{ b }+\overrightarrow{ c }=-\overrightarrow{ a } $
$ |\overrightarrow{ a }|^2+|\overrightarrow{ b }|^2-2|\overrightarrow{ a }||\overrightarrow{ b }| \cos (\angle ACB )=|\overrightarrow{ c }|^2 $
$ \cos (\angle ACB )=\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}$
A
$\frac{33}{2^{32}}$
B
$\frac{33}{2^{29}}$
C
$\frac{33}{2^{28}}$
D
$\frac{33}{2^{27}}$
Solution
$n p+n p q=24 ....$(1)
$n p \cdot n p q=128....$(2)
Solving (1) and (2):
We get $p =\frac{1}{2}, q =\frac{1}{2}, n =32$.
Now,
$P ( X =1)+ P ( X =2) $
$={ }^{32} C _1 pq ^{31}+{ }^{32} C _2 p ^2 q ^{30} $
$=\frac{33}{2^{28}}$
A
$\frac{17}{36}$
B
$\frac{4}{9}$
C
$\frac{1}{2}$
D
$\frac{19}{36}$
Solution
$ x ^2+\alpha x +\beta>0, \forall x \in R$
$ D =\alpha^2-4 \beta<0 $
$ \alpha^2<4 \beta$
Total cases$ = 6 \times 6=36 $
Fav. cases $=\beta=1, \alpha=1 $
$ \beta=2, \alpha=1,2 $
$ \beta=3, \alpha=1,2,3 $
$ \beta=4, \alpha=1,2,3$
$ \beta=5, \alpha=1,2,3,4 $
$ \beta=6, \alpha=1,2,3,4$
Total favourable cases $=17 $
$ P ( x )=\frac{17}{36}$
A
$5(2 \sqrt{3}+3) m$
B
$5(\sqrt{3}+3) m$
C
$10(\sqrt{3}+1) m$
D
$10(2 \sqrt{3}+1) m$
Solution

$ \frac{15}{ AQ }=\tan 60^{\circ}$
$\frac{15+x}{ AQ }=\tan 75^{\circ} $
$ \frac{(1)}{(2)} \Rightarrow x=10 \sqrt{3}$So, $P Q=5(2 \sqrt{3}+3) m$
A
$((\sim p) \vee q) \Rightarrow p$
B
$p \Rightarrow((\sim p ) \vee q )$
C
$((\sim p ) \vee q ) \Rightarrow q$
D
$q \Rightarrow((\sim p) \vee q)$

Answer: 7
Solution
$ A= \begin{bmatrix} 2 & -1 & -1 \\1 & 0 & -1 \\ 1 & -1 & 0\end{bmatrix} \Rightarrow A^2=A \Rightarrow A^n=A $
$ \forall n \in\{1,2, \ldots, 100\} $
Now, $ B = A - I =\begin{bmatrix} 1 & -1 & -1 \\1 & -1 & -1 \\1 & -1 & -1\end{bmatrix} $
$B ^2 =- B $
$\Rightarrow B ^3 =- B ^2= B$
$ \Rightarrow B ^5= B$
$\Rightarrow B ^{99}= B$
Also, $\omega^{3 k }=1$
So, $n =$ common of $\{1,3,5, \ldots, 99\}$ and $\{3,6,9, \ldots, 99\}=17$
Answer: 6006
Solution
$\left( t ^2 x ^{\frac{1}{5}}+\frac{(1- x )^{\frac{1}{10}}}{ t }\right)^{15} $
$ T _{ r +1}={ }^{15} C _{ r }\left( t ^2 x ^{\frac{1}{5}}\right)^{15- r } \cdot \frac{(1- x )^{\frac{ r }{10}}}{ t ^{ r }}$
For independent of $t$,
$30-2 r - r =0 $
$ \Rightarrow r =10$
So, Maximum value of ${ }^{15} C _{10} x (1- x )$ will be at
$x =\frac{1}{2}$
i.e. $6006$
Answer: 38
Solution
$ x^2-8 a x+2 a=0 $
$p+r=8 a $
$p r=2 a$
$ \frac{1}{p}+\frac{1}{r}=4 $
$\frac{2}{q}=4 $
$ q=\frac{1}{2} $
$ p=\frac{1}{5}$
$ x^2+12 b x+6 b=0 $
$ q+s=-12 b$
$ q s=6 b $
$\frac{1}{q}+\frac{1}{s}=-2$
$ \frac{2}{r}=-2$
$ r =-1 $
$ s=\frac{-1}{4}$
Now, $\frac{1}{ a }-\frac{1}{ b }=\frac{2}{ pr }-\frac{6}{ qs }=38$
Answer: 27560
Solution
$ a _1= b _1=1$
$ a _2= a _1+2=3 $
$ a _3= a _2+2=5$
$ a _4= a _2+2=7$
$ \Rightarrow a _{ n }=2 n -1 $
$ b _2= a _1+ b _1=4 $
$ b _3= a _3+ b _2=9 $
$ b _4= a _4+ b _3=16$
$ b _{ n }= n ^2$
$ \displaystyle\sum_{n=1}^{15} a_n b_n $
$ \displaystyle\sum_{n=1}^{15}(2 n-1) n^2$
$ \displaystyle\sum_{n=1}^{15}\left(2 n^3-n^2\right)$
$=2 \frac{n^2(n+1)^2}{4}-\frac{n(n+1)(2 n+1)}{6} $
Put $ n=15 $
$ =\frac{2 \times 225 \times 16 \times 16}{4}-\frac{15 \times 16 \times 31}{6}=27560$
Answer: 5
Solution
LHS
$ \displaystyle\lim _{n \rightarrow \infty} \frac{(n+1)^{k-1}}{n^{k+1}}[n k \cdot n+1+2+\ldots+n] $
$ = \displaystyle\lim _{n \rightarrow \infty} \frac{(n+1)^{k-1}}{n^{k+1}} \cdot\left[n^2 k+\frac{n(n+1)}{2}\right]$
$= \displaystyle\lim _{n \rightarrow \infty} \frac{( n +1)^{ k -1} \cdot n ^2\left( k +\frac{\left(1+\frac{1}{ n }\right)}{2}\right)}{ n ^{ k +1}}$
$ \Rightarrow \displaystyle\lim _{n \rightarrow \infty}\left(1+\frac{1}{n}\right)\left(k+\frac{\left(1+\frac{1}{n}\right)}{2}\right) $
$\Rightarrow\left(k+\frac{1}{2}\right) $
$ \text { RHS }$
$ \Rightarrow \displaystyle\lim _{ n \rightarrow \infty} \frac{1}{n^{ k +1}}\left(1^{ k }+2^{ k }+\ldots+ n ^{ k }\right)=\frac{1}{ k +1} $
$ \text { LHS }=\text { RHS } $
$ \Rightarrow k +\frac{1}{2}=33 \cdot \frac{1}{ k +1} $
$ \Rightarrow(2 k +1)( k +1)=66 $
$ \Rightarrow( k -5)(2 k +13)=0 $
$ \Rightarrow k =5 \text { or }-\frac{13}{2}$
Answer: 2
Solution
$ 2 p + f -1=0 .....$(1)
$2-p f -4 p =0 .....$(2)
$ 2=p( f +4) $
$ p =\frac{2}{ f +4} $
$ 2 p =1- f $
$ \frac{4}{ f +4}=1- f $
$ f ^2+3 f =0$
$ f =0 \text { or }-3$
Hyperbola $3 x^2-y^2=3, x^2-\frac{y^2}{3}=1$
$y = mx \pm \sqrt{ m ^2-3}$
It passes $(1,0)$
$o = m \pm \sqrt{ m ^2-3}$
$m$ tends $\infty$
It passes $(1,3)$
$ 3=m \pm \sqrt{m^2-3}$
$ (3-m)^2=m^2-3$
$m=2$
Answer: 10
Solution
$x^2=\frac{64.5}{75}\left(y-\frac{3}{5}\right)$
equation of tangent at $\left(\frac{8}{5}, \frac{6}{5}\right)$
$x \cdot \frac{8}{5}=\frac{64}{15}\left(\frac{y+\frac{6}{5}}{2}-\frac{3}{5}\right)$
$3 x-4 y=0$
equation of family of circle is
$\left(x-\frac{8}{5}\right)^2+\left(y-\frac{6}{5}\right)^2+\lambda(3 x-4 y)=0$
It touches $y$ axis so $f ^2= c$
$ x^2+y^2+x\left(3 \lambda-\frac{16}{5}\right)+y\left(-4 \lambda-\frac{12}{5}\right)+4=0$
$ \frac{\left(4 \lambda+\frac{12}{5}\right)^2}{4}=4 $
$ \lambda=\frac{2}{5} \text { or } \lambda=-\frac{8}{5} $
$ \lambda=\frac{2}{5}, r=1 $
$ \lambda=-\frac{8}{5}, r=4 $
$ d_1+d_2=10$
Answer: 3