Download our FREE NEET & JEE Prep App!!
Get Android App
Get iOS App
NEET 2020 Chemistry Questions with Answers Key Solutions
Solution:
Species in which bond order is zero do not exist.
(1) $O_2 = (KK)(\sigma 2s^2)(\sigma^* 2s^2)(\sigma 2p_z^2)$
$(\pi 2p_x^2 = \pi 2p_y^2)( \pi^* 2p_x^1 = \pi^* 2p_y^1)$
Bond Order $ = \frac{10 - 6}{2} = 2$
(2) $He_2 = (\sigma 1s^2)(\sigma^* 1s^2)$
Bond Order $= 0$
(3) $Li_2 = (\sigma1s^2)(\sigma^* 1s^2)(\sigma^* 2s^2)$
Bond Order $= 1$
(4) $C_2 = (\sigma 1s^2)(\sigma^* 1s^2)(\sigma 2s^2)(\sigma^* 2s^2)$
$(\pi 2p_x^2 = \pi 2p_y^2)$
Bond Order $= 2$
As, bond order of $He_2$ is zero it does not exist.
Solution:
$Ni(OH)_2 \rightleftharpoons \underset{(S)}{Ni^{2+}} + \underset{(2S)}{2OH^-} S =$ molar conc. of $Ni(OH)_2$
$NaOH \rightarrow Na^+ +\underset{(0.1\,M}{OH^-}$
$K_{SP} = [Ni^{2+}][OH^-]^2$
$ = (S)(2S + 0.1)^2$
$=(S)(4S^2 + 0.01 + 0.4S)$
$= 4S^3 + 0.01S + 0.4 S^2$
Neglecting higher power of $S$,
$2 \times 10^{-15} = 0.01S$
$S = 2 \times 10^{-13}M$
Solution:
(1) $CO_2(s)$ (dry ice) [not $CO_2(g)$] is used as refrigerant for ice cream and frozen food.
(2) The structure of $C_{60}$ contains $20$ six carbon rings and $12$ five carbon rings.
(3) $ZSM-5$ (a type of zeolite) is used to convert alcohols directly into gasoline.
(4) $CO(g)$ is colourless and adourless gas
Solution:
$\Delta G^{\circ} = -RT\,ln\,K_C$
$\Delta G^{\circ} = -8.314 \times 300 \,ln ( 2 \times 10^{13})$
Solution:
Atomic number
Name
IUPAC offical name
101
Unnilunium
Mendelevium
103
Unniltrium
Lawrencium
106
Unnilhexium
Seaborgium
111
Unununnium
Roentgenium
Element $(Z = 110)$ is ununnilium and its IUPAC offical name is Darmstadtium.
| Atomic number | Name | IUPAC offical name |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | Unnilunium | Mendelevium |
| 103 | Unniltrium | Lawrencium |
| 106 | Unnilhexium | Seaborgium |
| 111 | Unununnium | Roentgenium |
Solution:
In bcc unit cell, atoms lying along a body diagonal touch each other
Length of body diagonal $=\sqrt{3}a$
$\sqrt{3}a=4r$

$r=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}a$
As $a=288\,pm$
$\therefore r=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\times288Pm$
Solution:
The species with polar bonds and shall be non polar i.e., have zero dipole moment if resultant of all dipoles is cancelled due to symmetrical structure.

Solution:
Dissociation of sulfuric acid,
$H _{2} SO _{4} \rightarrow 2 H ^{+}( aq )+ SO _{4}^{-2}( aq )$
Disssociation of water,
$H _{2} O \rightarrow H ^{+}( aq )+ OH ^{-}( aq )$
At Anode : $4 OH ^{-} \rightarrow 2 H _{2} O ^{+}( l )+ O _{2}( g )+4 e ^{-}$
At Cathode: $2 H ^{+}( aq )+2 e ^{-} \rightarrow H _{2}( g )$
Solution:

Download our FREE NEET & JEE Prep App!!
Get Android App
Get iOS App
Solution:
Oxyacid
Structure
(1)
$H_{2}S_{2}O_{7}$

(2)
$H_{2}SO_{3}$ (Sulphurous acid)

(3)
$H_{2}SO_{4}$ (Sulphuric acid)

(4)
$H_{2}S_{2}O_{8}$

| Oxyacid | Structure | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | $H_{2}S_{2}O_{7}$ |  |
| (2) | $H_{2}SO_{3}$ (Sulphurous acid) |  |
| (3) | $H_{2}SO_{4}$ (Sulphuric acid) |  |
| (4) | $H_{2}S_{2}O_{8}$ |  |
Solution:
The Carbylamine test is a test for the detection of primary amines. (both aliphatic and aromatic amines)
In this test, the analyte is heated with alcoholic potassium hydroxide and chloroform.
If a primary amine is present, the foul smelling compound isocyanide is formed.
$
R - NH _{2}+ CHCl _{3}+3 KOH \rightarrow RN ^{+} \equiv C ^{-}+3 KCl +3 H _{2} O
$
Solution:
Electronic configuration of $Cr=[Ar]3d^{5}\,4s^{1}$
Electronic configuration of $Cr^{+2}=[Ar]3d^{4}$
Number of unpaired electrons $= 4$
Spin only magnetic moment $=\sqrt{n\left(n+2\right)}BM $ as $n=4$
$\therefore \mu=\sqrt{4\left(4+2\right)}$
$=\sqrt{24}$
$=4.90\,BM$
Solution:
For free expansion of ideal gas $P _{ e x t }= 0$
$W _{ p v }= 0$
$q = 0$ (adiabatic process)
$\Delta E = q + w$
$\Delta E = 0$
$\Delta E = n C _{ v m } \Delta T = 0$
$q = 0 , \Delta \mathbf { T } = 0 , w = 0$
Solution:
$\Delta\,T_{f}=iK_{f}m$
As solute is non-electrolyte, $i = 1$
$\Delta\,T_{f}=1\times 5.12\times 0.078$
$=0.40\,K$
Solution:
$
\begin{array}{l}
w = ZQ \\
Q =\frac{ w }{ Z }=\frac{20}{40 / 2} F =1 F
\end{array}
$
where $Z=\frac{E}{F}$
Solution:


This reactions carried out between two different aldehydes and/or ketones is called cross aldol condensation
Solution:
Paper Chromatography is a type of partition chormatography. Chormatography paper contains water trapped in it, which acts as the stationary phase. The paper selectively retains different components according to their differing partition in two phases.
Solution:
Collision frequency $\propto$ number of reactant molecules per unit volume
As concentraction o f reactants o f a reaction increase the number of reactant molecules per unit volume increase which increases the collision frequency
Solution:
Partial presure of $N_2 =$ mole fraction $\times P_{Total}$ of $N_2$
$X_{N_2} = \frac{\text{moles of }N_2}{\text{ total moles}}$
moles of $N_2 = \frac{7}{28} = \frac{1}{4};$
moles of $Ar = \frac{8}{40} = \frac{1}{5}$
$X_{N_2} = \frac{(\frac{1}{4})}{\frac{1}{4} + \frac{1}{5}} = \frac{5}{9}$
$P_{N_2} = \frac{5}{9} \times 27 = 15 $ bar
Download our FREE NEET & JEE Prep App!!
Get Android App
Get iOS App
Solution:
(1) Pig iron contains about 4% carbon and many impurities in smaller amount (e.g., S, P, Si, Mn). It can be moulded into variety o f shapes
(2) Wrought iron is the purest form o f carbon
(3) Blister copper has blistered appearance due to evolution of $SO_{2}$
(4) Vapour phase refining is carried out for nickel by Mond’s process
Solution:

Tertiary carbocations are stable due to inductive effect (+I effect of alkyl groups) and hyperconjugation.
Tert. carbocation has greater number of alpha H in comparison to sec carbocation. This increases hyperconjugation which results to its greater stability.
Solution:

Sodium dodecyl benzene sulphonate (anionic detergent)
(2) $CH_{3}(CH_{2})_{10}CH_{2}OSO^{-}_{3}Na^{+}$
Sodium lauryl sulphate (anionic detergent)
(3) $C_{17}H_{35}COONa$
Sodium stearate (Soap)

Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (Cationic detergent)
Solution:
This reaction is an example of $\beta$-elimination.Hydrogen is removed from $\beta-$ carbon and halogen from $\alpha$-carbon, hence dehydrohalogenation reaction.
Pent-2-ene is major product known as Saytzeff's product and it is more stable alkene than Pent-1-ene.
Generally, in $E _{2}$ reaction Zaitsev alkene is formed as a major product (more stable alkene).

Solution:
Solutions
Type
(1)
Chloroethane + Bromoethane
Ideal Solutions
(2)
Ethanol + Acetone
Nonideal (+ve deviation)
(3)
Benzene + Toluene
Ideal solutions
(4)
Acetone+$CHCl_{3}$
Nonideal (-ve deviation)
| Solutions | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | Chloroethane + Bromoethane | Ideal Solutions |
| (2) | Ethanol + Acetone | Nonideal (+ve deviation) |
| (3) | Benzene + Toluene | Ideal solutions |
| (4) | Acetone+$CHCl_{3}$ | Nonideal (-ve deviation) |
Solution:
Arrangement o f different ligands in increasing order of field strength called spectrochemical series is as follows:
$I^{-}<\,SCN^{-}<\,Cl^{-}<\,S^{2-}<\,F^{-}<\,OH^{-}<\,C_{2}O^{2-}_{4}<\,H_{2}O<\,NH_{3}<\,CN^{-}<\,CO$
Solution:
Amine
Structure
Nature
Lysine

Basic (As it contains more number of - $NH_{2}$ groups as composed to $-COOH$ group)
Serine

Neutral
Alanine

Neutral
Tyrosine

Neutral
| Amine | Structure | Nature |
|---|---|---|
| Lysine |  |
Basic (As it contains more number of - $NH_{2}$ groups as composed to $-COOH$ group) |
| Serine |  |
Neutral |
| Alanine |  |
Neutral |
| Tyrosine |  |
Neutral |
Solution:
On passing $HCl$ through aqueous solution of $CaCl_2, MgCl_2$ and $NaCl$, crystals of pure $NaCl$ seperate out. Calcium and magnesium chloride being more soluble than $NaCl$, remain in solution.
Solution:
$CO$ is formed by incomplete combustion. It forms stable complex with $O_2$ called carboxyhaemoglobin which is more stable than oxyhaemoglobin and it reduces oxygen carrying ability of blood.
Download our FREE NEET & JEE Prep App!!
Get Android App
Get iOS App
Solution:
$C_{12}H_{22}O_{11}+H_{2}O \to\underset{\text{D(+)Glucose}}{{C_{6}H_{12}O_{6}}}+\underset{\text{D(-)fructose}}{{C_{6}H_{12}O_{6}}}$
Sucrose contains two monosaccharides i.e., $\alpha-D$ glucose and $\beta-D-$ fructose which are obtained on its hydrolysis
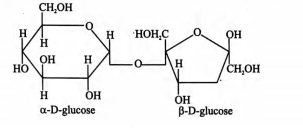
Solution:
Potassium ions are the most abundant cations within cell fluids where they activate many enymes, participate in the oxidation of glucose to produce ATP and with sodium are responsible for transmission of nerve signals.
Solution:
Number of atoms in $1\,g$ of $Li = \frac{1}{7} \times N_A$
$ = 0.86 \times 10^{23}$
Number of atoms in $1\, g$ of $Ag = \frac{1}{108} \times N_A$
$ = 0.056 \times 10^{23}$
Number of atoms in $1\,g$ of $Mg = \frac{1}{24} \times N_A$
$= 0.25 \times 10^{23}$
Number of atoms in $1\,g$ of $O_2 = \frac{1}{32} \times N_A \times 2 $
$= \frac{N_A}{16} = 0.37 \times 10^{23}$
Maximum number of atoms are present in$1\,g$ of $Li$.
Solution:
$^{175} Lu_{71} $ Number of electrons
= Number of protons $= 71$
Number of neutrons $= 175 - 71 = 104$
Solution:
Oxidation number of $C$ in $CH_4$ is $- 4$
as $x + 4 = 0$$\,\, x = - 4 (x$ is oxidation state of carbon)
oxidation of $C$ in $CCl_4$ is $+ 4$
as $x - 4 = 0 \,\,\,x = + 4$
$\therefore $ Change in oxidation state of carbon is from $-4$ to $+4$
Solution:
Chromate $\left( CrO _{4}^{-2}\right) \Rightarrow$ oxidation state $=+6$
Dichromate $\left( Cr _{2} O _{7}^{-2}\right) \Rightarrow$ oxidation state $=+6$
Oxidation states are same.
All other statements are correct except on oxidation states of chromium.
Solution:
$2 C l(g) \longrightarrow C l_2(g)$
As the process involves bond formation $\Delta H=-v e$ and as the number of gaseous particles are decreasing in the reaction $\Delta S$ is also $-v e$
i.e., $\Delta_r H< 0$ and $\Delta_r S< 0$
Solution:
Greater the Zeta potential more will be the stability of colloidal particles as there will be a balance between the repulsive interactions between the charges of electrical double layer and attractive van der Waal interactions between molecules
Solution:
$NH_{2}CONH_{2}+H_{2}O \to$
$\underset{(A)}{(NH_{4})_{2}CO_{3}} \rightleftharpoons \underset{(B)}{2NH_{3}}+H_{2}O+CO_{2}$
$\underset{(B)}{4NH_{3}}+\overset{2+}{Cu(aq)} \to \underset{\text{(deep blue (C)}}{\left[Cu\left(NH_{3}\right)_{4}\right]_{\left(aq\right)}^{2+}}$
Solution:
a
$CO + H_2$
iii
Synthesis gas
b
Temporary hardness of water
i
$Mg(HCO_3)_2 + Ca(HCO_3)_2$
c
$B_2H_6$
ii
An electron deficient hydride
d
$H_2O_2$
iv
Non planar structure

| a | $CO + H_2$ | iii | Synthesis gas |
| b | Temporary hardness of water | i | $Mg(HCO_3)_2 + Ca(HCO_3)_2$ |
| c | $B_2H_6$ | ii | An electron deficient hydride |
| d | $H_2O_2$ | iv | Non planar structure 
|
Download our FREE NEET & JEE Prep App!!
Get Android App
Get iOS App
Solution:
Oxide
Nature
(a)
CO
(ii)
Neutral
(b)
BaO
(i)
Basic
(c)
$Al_{2}O_{3}$
(iv)
Amphoteric
(d)
$Cl_{2}O_{7}$
(iii)
Acidic
| Oxide | Nature | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | CO | (ii) | Neutral |
| (b) | BaO | (i) | Basic |
| (c) | $Al_{2}O_{3}$ | (iv) | Amphoteric |
| (d) | $Cl_{2}O_{7}$ | (iii) | Acidic |
Solution:
$K=\frac{2.303}{t}log\, \frac{a}{a-x}$
$t=\frac{2.303}{4.606\times 10^{-3}}$
$log\,\frac{2}{0.2}$
$=\frac{1000}{2} \,\log\,10$
$=500\,\sec$
(as log $10=1)$
Solution:
$n$-butane, $n$-hexane, $2,3$-dimethylbutane are symmetrical alkanes. Such alkanes are prepared in good yield by Wurtz reaction as these require single alkyl halide for their preparation.
$CH_3CH_2Cl \xrightarrow[\text{dry ether}]{+2\,Na} \underset{\text{(n-butane)}}{CH_3CH_2CH_2CH_3}$
$CH_3CH_2CH_2Cl \xrightarrow[\text{dry ether}]{+2\,Na}$
$ \underset{\text{(n-hexane)}}{CH_3CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_3}$
$CH_3- \underset{\overset{|}{CH_3}}{CH}-Cl \xrightarrow[\text{dry ether}]{+2\,Na}\underset{\text{(2,3 -Dimethyl butane)}}{CH_3-\underset{\overset{|}{CH_3}}{CH}-\underset{\overset{|}{CH_3}}{CH} - CH_3}$
$n$-heptane is an unsymmetrical alkane that requires two different alkyl halides for its preparation. This will form three different alkanes, thus, lowering the yield of required alkane.
$CH_3CH_2CH_2Cl + CH_3CH_2CH_2CH_2Cl \xrightarrow[\text{dry ether}]{+2\,Na}$
$CH_3CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_3 $
$+ CH_3CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_3$
$+CH_3CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_3$
Solution:

Reaction is $S_{N}2$ reaction in which $I^{-}$ ttacks at alkyl group with lesser steric hindrance and weak $C-O$ bond
Download our FREE NEET & JEE Prep App!!
Get Android App
Get iOS App