- Tardigrade
- Question
- Physics
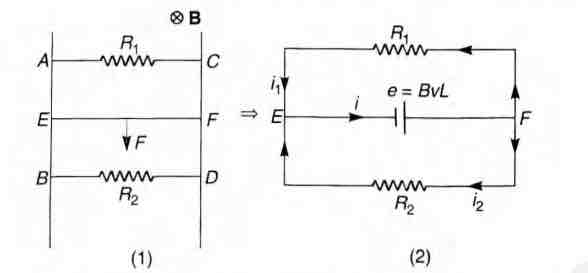
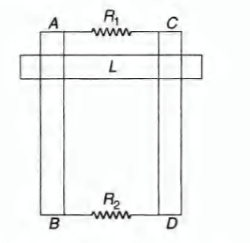
- Two parallel vertical metallic rails AB and CD are separated by 1 m. They are connected at two ends by resistances R1 and R2 as shown in figure. A horizontal metallic bar of mass 0.2 kg slides without friction vertically down the rails under the action of gravity. There is a uniform horizontal magnetic field of 0.6 T perpendicular to the plane of the rails. It is observed that when the terminal velocity is attained, the powers dissipated in R1 and R2 are 0.76 W and 1.2 W respectively. Find the terminal velocity of the bar L and the values of R1 and R2
Q.
Two parallel vertical metallic rails and are separated by . They are connected at two ends by resistances and as shown in figure. A horizontal metallic bar of mass slides without friction vertically down the rails under the action of gravity. There is a uniform horizontal magnetic field of perpendicular to the plane of the rails. It is observed that when the terminal velocity is attained, the powers dissipated in and are and respectively. Find the terminal velocity of the bar and the values of and
Solution:
Let the magnetic field be perpendicular to the plane of rails and inwards.
If be the terminal velocity of the rails, then potential difference across E and F would be with at lower potential and at higher potential.
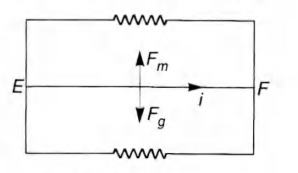
The equivalent circuit is shown in figure (2). In figure (2)
..(i)
..(ii)
Power dissipated in is
Therefore ..(iii)
Similarly, ..(iv)
Now the total current in bar is
( from to ) ...( v)
or
Multiplying Eq. (v) by e, we get
[From Eqs. (iii) and (iv)]
or
But since
.
Hence, terminal velocity of bar is .
Power in is
Similarly,
.