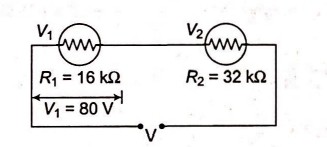
Q. Voltmeters $V_{1}$ and $V_{2}$ are connected in series across a D.C. line. $V_{1}$ reads $80$ volts and has a per volt resistance of $200$ ohms. $V_{2}$ has a total resistance of $32$ kilo-ohms. The line voltage is
Current Electricity
Solution: