Q.
The figure below is the plot of potential energy versus internuclear distance $(d)$ of $H _{2}$ molecule in the electronic ground state. What is the value of the net potential energy $E_{0}$ (as indicated in figure) in $kJ\, mol ^{-1}$, for $d=d_{0}$ at which the electron-electron repulsion and the nucleus-nucleus repulsion energies are absent? As reference, the potential energy of $H$ atom is taken as zero when its electron and the nucleus are infinitely far apart.
Use Avogadro constant as $6.023 \times 10^{23} mol ^{-1}$.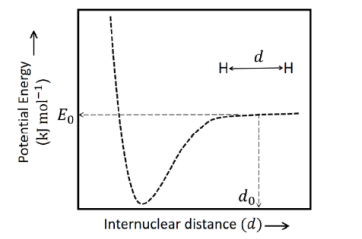
JEE AdvancedJEE Advanced 2020
Solution: