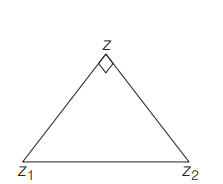Q. If $z_{1}=2-3 i$ and $z_{2}=-1+i$, then the locus of a point $P$ represented by $z=x+i y$ in the argand plane satisfying the equation $\arg \left(\frac{z-z_{1}}{z-z_{2}}\right)=\frac{\pi}{2}$ is
TS EAMCET 2018
Solution: