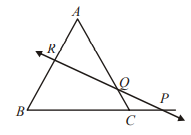
Q. A line $L$ intersects the three sides $B C, C A$ and $A B$ of a $\Delta A B C$ at $P, Q$ and $R$ respectively. Then, $\frac{B P}{P C} \cdot \frac{C Q}{Q A} \cdot \frac{A R}{R B}$ is equal to
Straight Lines
Solution: