- Tardigrade
- Question
- Biology
- The given graph shows length-tension curve for a typical vertebrate sarcomere. <img class=img-fluid question-image alt=Question src=https://cdn.tardigrade.in/q/nta/b-wzx1mhzyqn3ubq2u.jpg /> By analysing the graph, what can you deduce regarding the muscle contraction? (i) Neither the myosin filaments nor the actin thin filaments change in length when a sarcomere shortens or is stretched. Instead, it is the extent of overlap between actin and myosin filaments that changes. (ii) The total tension produced by a sarcomere is proportional to the total number of cross-bridges that can interact with actin filaments, and this number in turn is proportional to the amount of overlap between thick and thin filaments. (iii) The tension produced by the muscle is maximal when the overlap between thick and thin filaments allows the largest number of myosin cross-bridges to bind to actin. (iv) Tension drops off with increased length, because the thick and thin filaments overlap less and fewer cross-bridges can bind. (v) Tension drops off with decreased length, because thin filaments at the two ends of the sarcomere begin to collide with each other, preventing further shortening.
Q.
The given graph shows length-tension curve for a typical vertebrate sarcomere.
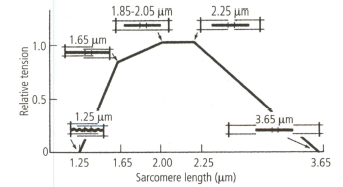
By analysing the graph, what can you deduce regarding the muscle contraction?
(i) Neither the myosin filaments nor the actin thin filaments change in length when a sarcomere shortens or is stretched. Instead, it is the extent of overlap between actin and myosin filaments that changes.
(ii) The total tension produced by a sarcomere is proportional to the total number of cross-bridges that can interact with actin filaments, and this number in turn is proportional to the amount of overlap between thick and thin filaments.
(iii) The tension produced by the muscle is maximal when the overlap between thick and thin filaments allows the largest number of myosin cross-bridges to bind to actin.
(iv) Tension drops off with increased length, because the thick and thin filaments overlap less and fewer cross-bridges can bind.
(v) Tension drops off with decreased length, because thin filaments at the two ends of the sarcomere begin to collide with each other, preventing further shortening.
Solution:
Actin (thin) filament is made up of two F actins helically wound to each other. Each F actin is a polymer of monomeric G (globular) actin. Two filaments of tropomyosin also run close to F actin throughout its length. A complex protein troponin is distributed at regular interval on tropomyosin.
Myosin (thick) filament is also a polymerised protein. Much monomeric protein called meromyosin constitutes one thick filament. Each meromyosin has two important part: a) Globular head - heavy meromyosin with a short arm. b) tail- light meromyosin
The head and short arm of meromyosin are projected upward. The globular head is an active ATPase enzyme and has a binding site for ATP and functional areas for actin.
Mechanism of action:- mechanism of muscle contraction is best explained by the ''sliding filament theory''. which states that '' the contraction of a muscle fibre takes place by the sliding of the thin filaments.''
Sarcomere - contraction unit of muscle, contains 1/2 I band + 1 A band + 1/2 I band.
I band contain actin filament, and A band has myosin filaments connecting two sarcomeres is the Z line. So, the distance between the 2 Z line gives us the length of a sarcomere. On contraction due to unmasking and masking ATP sites on the globular head of myosin filament with troponin molecule on I band. Due to repeated masking and unmasking actin and myosin causes a decrease in muscle length decreases during contraction.
So, as the muscle having more number of sarcomere stronger will be the contraction of that muscle.
There is more overlapping of A, and I band to such extent that I band and A band remain at the same position on severe contraction. So, due to such I-I overlapping, the strong bond between A-I overlapping reduces, and thus, muscle tension decreases.
During relaxation Z-Z line distance increases, a reduced number of cross bridging between A and I band, which leads to reduced attachment and thus reduced muscle tension.
Myosin (thick) filament is also a polymerised protein. Much monomeric protein called meromyosin constitutes one thick filament. Each meromyosin has two important part: a) Globular head - heavy meromyosin with a short arm. b) tail- light meromyosin
The head and short arm of meromyosin are projected upward. The globular head is an active ATPase enzyme and has a binding site for ATP and functional areas for actin.
Mechanism of action:- mechanism of muscle contraction is best explained by the ''sliding filament theory''. which states that '' the contraction of a muscle fibre takes place by the sliding of the thin filaments.''
Sarcomere - contraction unit of muscle, contains 1/2 I band + 1 A band + 1/2 I band.
I band contain actin filament, and A band has myosin filaments connecting two sarcomeres is the Z line. So, the distance between the 2 Z line gives us the length of a sarcomere. On contraction due to unmasking and masking ATP sites on the globular head of myosin filament with troponin molecule on I band. Due to repeated masking and unmasking actin and myosin causes a decrease in muscle length decreases during contraction.
So, as the muscle having more number of sarcomere stronger will be the contraction of that muscle.
There is more overlapping of A, and I band to such extent that I band and A band remain at the same position on severe contraction. So, due to such I-I overlapping, the strong bond between A-I overlapping reduces, and thus, muscle tension decreases.
During relaxation Z-Z line distance increases, a reduced number of cross bridging between A and I band, which leads to reduced attachment and thus reduced muscle tension.