- Tardigrade
- Question
- Biology
- From the given graph, find out which of the following factors affect the enzyme activity? <img class=img-fluid question-image alt=Question src=https://cdn.tardigrade.in/q/nta/b-qlc0roddr3v3ucud.jpg /> (i) Temperature (ii) Substrate concentration (iii) pH (iv) Competitive inhibitor
Q.
From the given graph, find out which of the following factors affect the enzyme activity?
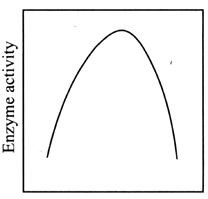
(i) Temperature
(ii) Substrate concentration
(iii) pH
(iv) Competitive inhibitor
Solution: