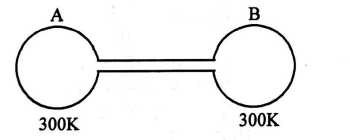
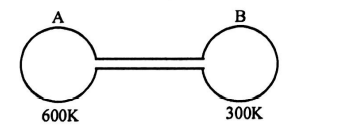
Q. Two spherical vessels of equal volume are connected by a narrow tube. The apparatus contains an ideal gas at one atmosphere and $300\, K$. Now if one vessel is immersed in a bath of constant temperature $600 \,K$ and the other in a bath of constant temperature $300 \,K$, then the common pressure will be -
Thermodynamics
Solution: