Q.
Two metallic rods $P Q$ and $Q R$ of different materials are joined together at the junction $Q$ as shown in figure. It is observed that if the ends $P$ and $R$ are kept at $100^{\circ} C$ and $0^{\circ} C$ respectively, the temperature of the junction $Q$ is $60^{\circ} C$. There is no loss of heat to the surroundings. The rod $Q R$ is replaced by another rod $Q R^{\prime}$ of the same material and length $\left(Q R=Q R^{\prime}\right)$. If the area of cross-section of $Q R^{\prime}$ is twice that of $Q R$ and the ends $P$ and $R^{\prime}$ are maintained at $100^{\circ} C$ and $0^{\circ} C$ respectively, the temperature of the junction $Q$ will be nearly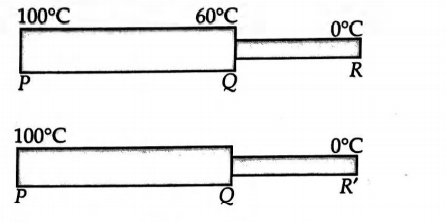
Thermal Properties of Matter
Solution:

