Q.
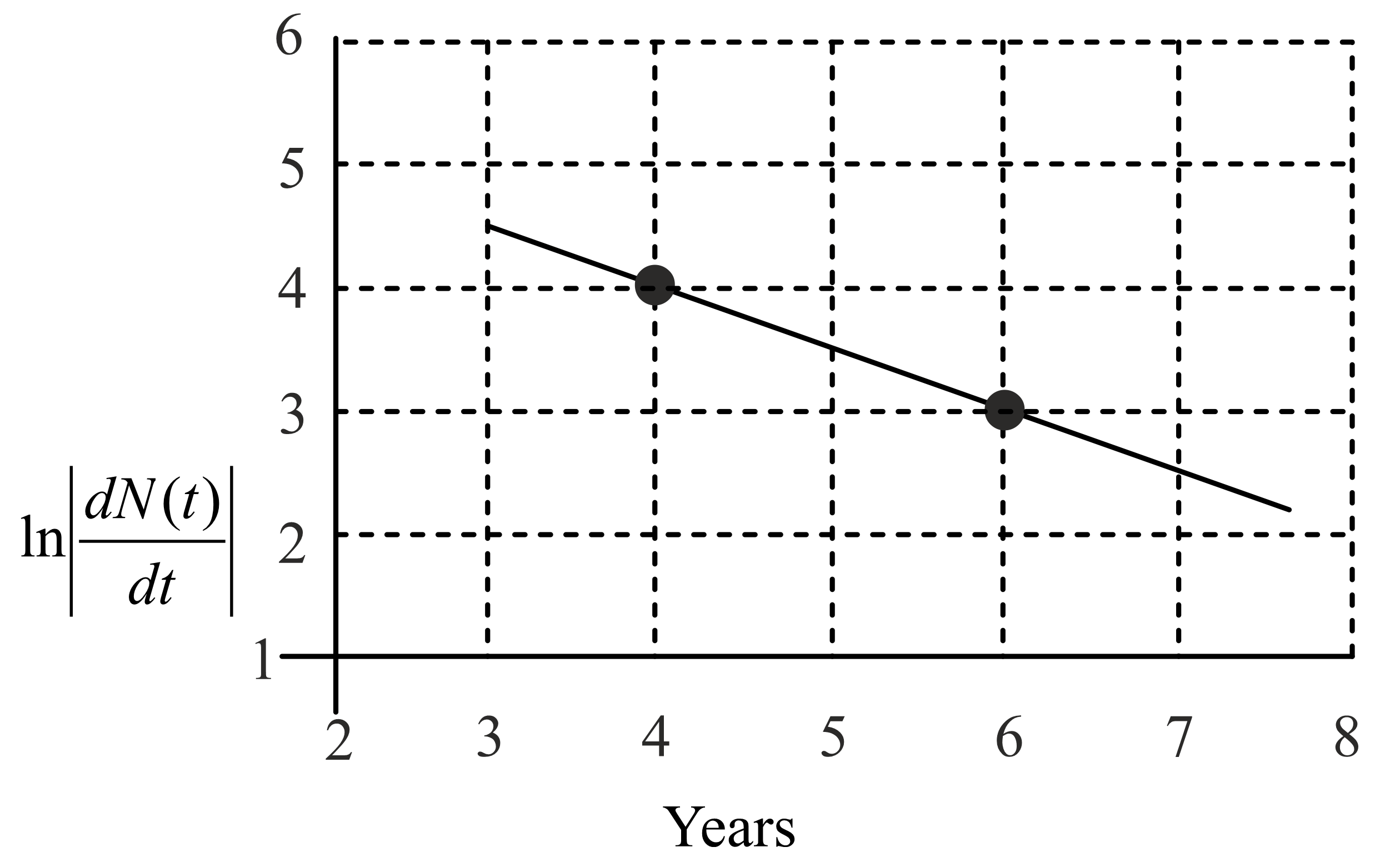
To determine the half life of a radioactive element, a student plots a graph of $\ln\frac{d N \left(\right. t \left.\right)}{d t}$ versus $t.$ Here, $\frac{d N \left(\right. t \left.\right)}{d t}$ is the rate of radioactive decay at time $t.$ If the number of radioactive nuclei of this element decreases by a factor of $p$ after $4.16$ years, the value of $p$ is:
NTA AbhyasNTA Abhyas 2022
Solution: