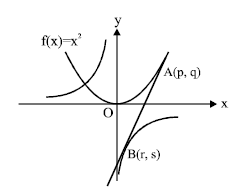
Q. There is a point $(p, q)$ on the graph of $f(x)=x^{2}$ and a point $(r, s)$ on the graph of $g(x)=\frac{-8}{x}$, where $p>$ 0 and $r>0$. If the line through $(p, q)$ and $(r, s)$ is also tangent to both the curves at these points, respectively, then the value of $p + r$ is
Application of Derivatives
Solution: