Q.

The thermodynamic cycle of an engine operating with an ideal monatomic gas is represented by the $P-V$ diagram as shown in the above figure. Find the efficiency and the amount of heat extracted from the source in a single cycle.
NTA AbhyasNTA Abhyas 2020
Solution:
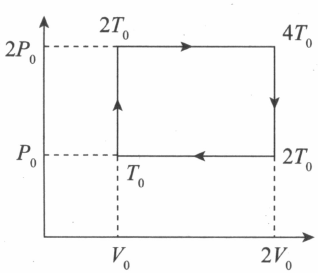
Let $Q$ be the heat extracted per cycle,
$C_{v}=$ specific heat at constant volume,
$C_{p}=$ specific heat at constant pressure
$Q=nC_{v}\left(d T\right)+nC_{p}\left(d T\right)\Rightarrow Q=nC_{v}\left(2 T_{0} - T_{0}\right)+nC_{p}\left(4 T_{0} - 2 T_{0}\right)$
For monoatomic gas,
$C_{v}=$ $\frac{f R}{2}$
$C_{p}=\frac{\left(\right. f + 2 \left.\right) R}{2}$
$C_{v}=\frac{3 R}{2},C_{p}=\frac{5 R}{2}$
$Q=\frac{n \left(\right. 3 R \left.\right) T_{0}}{2}+\frac{n 5 R}{2}\left(2 T_{0}\right)=\frac{13}{2}nRT_{0}$
$Q=\frac{13}{2}P_{0}V_{0}$
$W=$ area bounded by curve $=P_{0}V_{0}$
Let $\eta=$ efficiency during the cycle,
$\eta=\frac{W}{Q}\times 100\Rightarrow \eta=\frac{P_{0} V_{0}}{\frac{13 P_{0} V_{0}}{2}}\times 100\Rightarrow \eta=\frac{2}{13}\times 100\Rightarrow \eta=15.4\%$

Let $Q$ be the heat extracted per cycle,
$C_{v}=$ specific heat at constant volume,
$C_{p}=$ specific heat at constant pressure
$Q=nC_{v}\left(d T\right)+nC_{p}\left(d T\right)\Rightarrow Q=nC_{v}\left(2 T_{0} - T_{0}\right)+nC_{p}\left(4 T_{0} - 2 T_{0}\right)$
For monoatomic gas,
$C_{v}=$ $\frac{f R}{2}$
$C_{p}=\frac{\left(\right. f + 2 \left.\right) R}{2}$
$C_{v}=\frac{3 R}{2},C_{p}=\frac{5 R}{2}$
$Q=\frac{n \left(\right. 3 R \left.\right) T_{0}}{2}+\frac{n 5 R}{2}\left(2 T_{0}\right)=\frac{13}{2}nRT_{0}$
$Q=\frac{13}{2}P_{0}V_{0}$
$W=$ area bounded by curve $=P_{0}V_{0}$
Let $\eta=$ efficiency during the cycle,
$\eta=\frac{W}{Q}\times 100\Rightarrow \eta=\frac{P_{0} V_{0}}{\frac{13 P_{0} V_{0}}{2}}\times 100\Rightarrow \eta=\frac{2}{13}\times 100\Rightarrow \eta=15.4\%$