Q.
The sum of an infinitely decreasing geometric progression whose first term is a and common ratio $r$, is equal to least value of the quadratic trinomial $P ( x )=3 x ^2- x +\frac{25}{12}$, in [0,2]. Also the first term of the geometric progression is equal to the square of its common ratio.
If the minimum value of $P(x)$ lies between roots of equation $x^2+(k+1) x+a+2 \sqrt{3}=0$, then the maximum integral value of $k$ is
Sequences and Series
Solution:
$\therefore r =(\sqrt{3}-1) [\text { As } r \in(0,1)] $
$\Rightarrow a = r ^2=4-2 \sqrt{3}$
[As $r \in(0,1)]$
$\Rightarrow a = r ^2=4-2 \sqrt{3}$
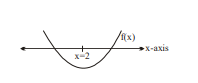
Let $f(x)=x^2+(k+1) x+a+2 \sqrt{3}$
Now, $f(x)=0 \Rightarrow a^2+(k+1) x+4=0$.
Since 2 lies between the roots, hence $f (2)<0$
$\Rightarrow 4+2 k +2+4<0 \Rightarrow 2 k +10<0 \Rightarrow k <-5$
So, $k _{\max .}=-6$.