Q.
The expression $y=a x^2+b x+c(a, b, c \in R$ and $a \neq 0)$ represents a parabola which cuts the $x$-axis at the points which are roots of the equation $ax ^2+ bx + c =0$. Column-II contains values which correspond to the nature of roots mentioned in column-I.
Column I
Column II
A
For $a =1, c =4$, if both roots are greater than 2 then $b$ can be equal to
P
4
B
For $a =-1, b =5$, if roots lie on either side of -1 then $c$ can be equal to
Q
8
C
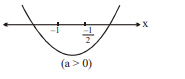
For $b=6, c=1$, if one root is less than -1 and the other root greater than (
R
10$\frac{-1}{2}$ then a can be equal to
S
no real value
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A | For $a =1, c =4$, if both roots are greater than 2 then $b$ can be equal to | P | 4 |
| B | For $a =-1, b =5$, if roots lie on either side of -1 then $c$ can be equal to | Q | 8 |
| C | For $b=6, c=1$, if one root is less than -1 and the other root greater than ( | R | 10$\frac{-1}{2}$ then a can be equal to |
| S | no real value | ||
Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Solution: