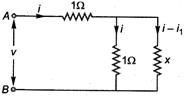
Q.
The equivalent resistance between points A and B of an infinite network of resistance s each of $ 1\,\Omega , $ connected as shown, is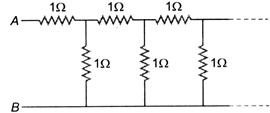
ManipalManipal 2008Current Electricity
Solution:
Let $ x $ be the equivalent resistance of entire network between $ A $ and $ B $ . Hence, we have
$ {{R}_{AB}}=1+ $ resistance of parallel combination of $ 1\Omega $ and $ x\Omega $
$ \therefore $ $ {{R}_{AB}}=1+\frac{x}{1+x} $
$ \therefore $ $ x=1+\frac{x}{1+x} $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ x+{{x}^{2}}=1+x+x $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ {{x}^{2}}-x-1=0 $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ x=\frac{1+\sqrt{1+4}}{2}=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\Omega $