Q.
Stomatal opening and closing involves the role of various ions. In the given figure, arrows depict the movement of certain ions during stomatal opening in light. Identify the ions (P, Q, R and S) and select the correct option.
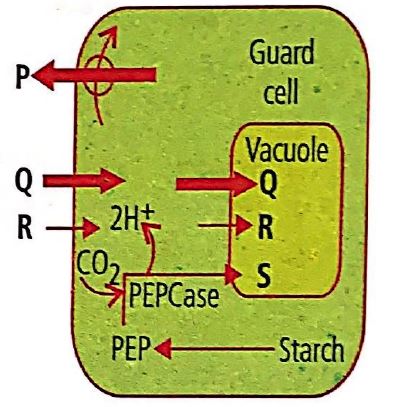
P
Q
R
S
(a)
Malate$^{2-}$
$K^+$
$Cl^-$
$H^+$
(b)
$K^+\,\,$
$H^+\,\,$
$Cl^-$
Malate$^{2-}$
(c)
$H^+\,\,$
$K^+\,\,$
$Cl^-\,\,$
Malate$^{2-}$
(d)
$K^+\,\,$
Malate$^{2-}$
$H^+\,\,$
$Cl^-$
| P | Q | R | S | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | Malate$^{2-}$ | $K^+$ | $Cl^-$ | $H^+$ |
| (b) | $K^+\,\,$ | $H^+\,\,$ | $Cl^-$ | Malate$^{2-}$ |
| (c) | $H^+\,\,$ | $K^+\,\,$ | $Cl^-\,\,$ | Malate$^{2-}$ | (d) | $K^+\,\,$ | Malate$^{2-}$ | $H^+\,\,$ | $Cl^-$ |
Transport in Plants
Solution: