Q.
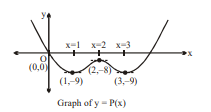
Let $P(x)$ be a polynomial of degree 4 having a relative maximum at $x=2$ and $\underset{x \rightarrow 0}{\text{Lim}} \left(3-\frac{P(x)}{x}\right)=27$. Also $P (1)=-9$ and $P ^{\prime \prime}( x )$ has a local minimum at $x =2$.
The absolute minimum value of function $y=P^{\prime}(x)$ on the set $A=\left\{x \mid x^2+12 \leq 7 x\right\}$ equals
Application of Derivatives
Solution: