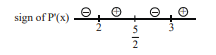Q. Let $\mathrm{P}(\mathrm{x})$ be a polynomial of degree 4 such that $\mathrm{P}(1)=7$ and attains its minimum value 3 at both $x=2$ and $x=3$. If local maximum value of $P(x)$ is $\frac{m}{n}$, where $m \& n$ are relatively prime natural numbers then find the value of $(m-3 n)$.
Application of Derivatives
Solution: