Q.
Let $a, b \in R$ be such that the function $f$ given by $f\left(x\right) = \ell n |x| + bx^{2} + ax, x \ne 0$ has extreme values at $ x = - 1$ and $x = 2$.
Statement-1 : $f$ has local maximum at $x = - 1$ and at $x = 2$.
Statement-2 : $a = \frac{1}{2}$ and $b = \frac{-1}{4}$
AIEEEAIEEE 2012Application of Derivatives
Solution:
$f'\left(x\right) = \frac{1}{x} + 2bx + a$
at $x = - 1 \quad-1 - 2b + a = 0$
$\quad a - 2b = 1\quad\quad ...\left(i\right)$
at $x = 2 \quad \frac{1}{2} + 4b + a = 0$
$\quad a + 4b = -\frac{1}{2}\quad\quad...\left(ii\right)$
On solving $\left(i\right)$ and $\left(ii\right) \quad a = \frac{1}{2}, b = \frac{1}{4}$
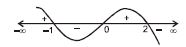
$f '\left(x\right) = \frac{1}{x} - \frac{x}{2}+\frac{1}{2} = \frac{2-x^{2}+x}{2x} = \frac{-\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}{2x}$
So maxima at $x = - 1, 2$