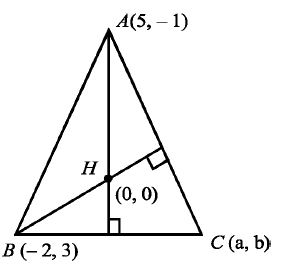
Q. If two vertices of a triangle are (5, -1) and (-2,3) and its orthocentre is at (0,0), then the third vertex is
AIEEEAIEEE 2012Straight Lines
Solution:
Let the third vertex of $\Delta$ ABC be $\left(a, b\right)$.
Orthocentre $= H\left(0,0\right)$
Let A $\left(5, - 1\right)$ and B $\left(- 2, 3\right)$ be other two
vertices of $\Delta$ ABC.
Now, (Slope of AH) $\times$ (Slope of BC) $=-1$
$\Rightarrow \quad\left(\frac{-1-0}{5-0}\right)\left(\frac{b-3}{a+2}\right) = -1$
$\Rightarrow \quad b - 3 = 5 \left(a + 2\right) \quad\quad...\left(1\right)$
Similarly,
(Slope of BH) $\times$ (Slope of AC) $= -1$
$\Rightarrow \quad-\left(\frac{3}{2}\right)\times\left(\frac{b+1}{a-5}\right) = -1$
$\Rightarrow \quad3h + 3 = 2a-10$
$\Rightarrow \quad3b-2a+13 =0\quad\quad ...\left(2\right)$
On solving equation (1) and (2) we get
$a = -4,b = -7$
Hence, third vertex is $\left(- 4,-7\right).$