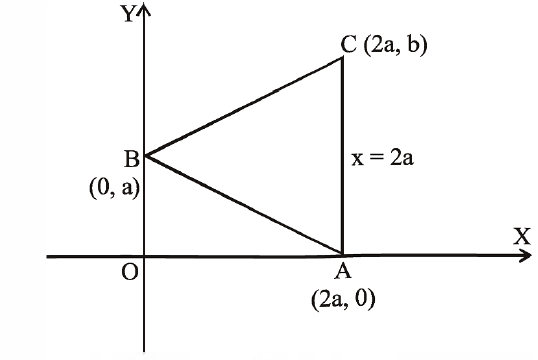
Q. If the extremities of the base of an isosceles triangle are the points $(2a, 0)$ and $(0, a)$ and the equation of one of the sides is $x = 2a$, then the area of the triangle, in square units, is :
Solution:
Let $y$-coordinate of $C =b$
$AB=\sqrt{4a^{2}+a^{2}}=\sqrt{5}a$
Now, $AC=BC \Rightarrow b=a^{2}\sqrt{4a^{2}+\left(b-a\right)^{2}}$
$b^{2}=4a^{2}+b^{2}+a^{2}-2ab$
$\Rightarrow 2ab=5a^{2} \Rightarrow b=\frac{5a}{2}$
$\therefore C=\left(2a, \frac{5a}{2}\right)$
Hence area of the triangle
$=\frac{1}{2}\begin{vmatrix}2a&0&1\\ 0&a&1\\ 2a&\frac{5a}{2}&1\end{vmatrix}=\frac{1}{2}\begin{vmatrix}2a&0&1\\ 0&a&1\\ 0&\frac{5a}{2}&0\end{vmatrix}$
$=\frac{1}{2}\times2a\left(-\frac{5a}{2}\right)=-\frac{5a^{2}}{2}$
Since area is always +ve, hence area
$=\frac{5a^{2}}{2}$ sq.unit