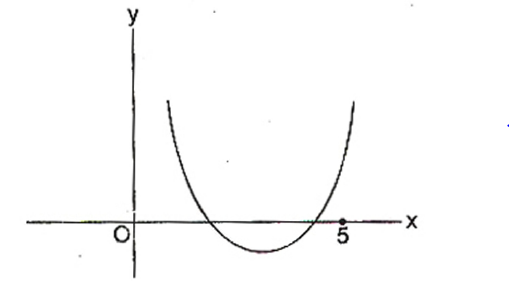
Q. If both the roots of the quadratic equation $x^2 - 2 kx + k^2 + k - 5 = 0$ are less than 5, then $k$ lies in the interval:
AIEEEAIEEE 2005Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Solution:
Key Idea : If both roots of $ax^2 + bx + c = 0$ are less then $\alpha$, then $b^{2}-4ac\ge0, f \left(\alpha\right) >0$ and $\frac{-b}{2a} < \alpha$
Let $f \left(x\right)=x^{2}-2kx+k^{2}+k-5$
$\therefore D=4k^{2}-4\left(k^{2}+k-5\right)$
$=-4k+20\ge0$
$\Rightarrow k\le5\,...\left(i\right)$
Also $-\frac{b}{2a}<5\,...\left(ii\right)$
and $f \left(5\right)>0\,...\left(iii\right)$
From $\left(ii\right), k < 5\,...\left(iii\right)$
From $\left(iii\right), 25 - 10k + k^{2} + k - 5>0$
$\Rightarrow k^{2}-9k+20>0$
$\Rightarrow k^{2} - 5k - 4k + 20 > 0$
$\Rightarrow \left(k - 5\right) \left(fc - 4\right) > 0$
$\Rightarrow k < 4 and k > 5\,...\left(v\right)$
From $\left(i\right), \left(iii\right)$ and $\left(iv\right)$
$\Rightarrow k<4$