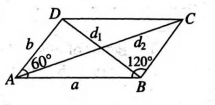
Q. Given a parallelogram whose acute angle is $60^{\circ}$, if the squares of length of the diagonals are in ratio $1: 3$ then $\frac{a}{b}$ is (where $a, b$ are the length of the sides)
Trigonometric Functions
Solution:
Applying cosine rule in $\triangle A B D$ and $\triangle A B C$,
we get $2 a^{2}+2 b^{2}=d_{1}^{2}+d_{2}^{2}$,
where $d_{1}, d_{2}$ are lengths of diagonals
$\left(d_{1}< d_{2}\right)$ given $d_{2}^{2}=3 d_{1}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow a^{2}+b^{2}=2 d_{1}^{2}$
Also $a b=d_{1}^{2}$ ...(1)
$\Rightarrow a^{2}+b^{2}+2 a b=4 d_{1}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow (a+ b)^{2}=4 d_{1}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow a+b=2 d_{1}$ ...(2)
Using (1) and (2), we get $a=b$ i.e., $\frac{a}{b}=1$.