Q.
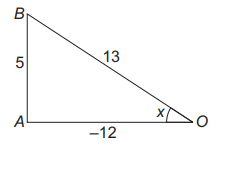
Consider the information given below $\tan x=-\frac{5}{12}$, where $x$ lies in second quadrant.
Statement I The values of $\cot x, \sin x, \cos x$, $\operatorname{cosec} x, \sec x$ are $\frac{-12}{5}, \frac{5}{13}, \frac{-12}{13}, \frac{13}{5}, \frac{-13}{12}$, respectively.
Statement II In second quadrant the value of $\sin x$ and $\operatorname{cosec} x$ are positive.
Choose the correct option.
Trigonometric Functions
Solution: