Q.
Column I
Column II
A
The lines $\left(y-y_1\right)=m\left(x-x_1\right) \pm 4 \sqrt{1+m^2}$ are tangents to the same circle. The radius of the circle is
P
4
B
A line $L$ passes through a point $P (1,2)$ and has negative gradient. If $L$ makes an angle of $\frac{\pi}{4}$ with the lines $2 x+3 y=10$, the y-intercept of the line $L$ is
Q
7
C
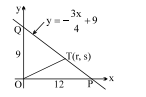
The line $y=-\frac{3 x}{4}+9$ crosses the $x$-axis at $P$ and the $y$-axis at $Q$. Point $T$ lies on $PQ$ and its coordinates are $( r , s )$. If $\frac{\text { Area of triangle } P O Q}{\text { Area of triangle TOP }}=3$, then the value of $(r+s)$ equals
R
8
D
Let $ABC$ be a triangle with $AB =3, BC =4$ and $AC =5$. Let $I$ be the centre of the circle inscribed in triangle $ABC$. The product of the distances of incentre from the vertices $A , B$ and $C$ of the triangle $ABC$, is
S
10
T
11
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A | The lines $\left(y-y_1\right)=m\left(x-x_1\right) \pm 4 \sqrt{1+m^2}$ are tangents to the same circle. The radius of the circle is | P | 4 |
| B | A line $L$ passes through a point $P (1,2)$ and has negative gradient. If $L$ makes an angle of $\frac{\pi}{4}$ with the lines $2 x+3 y=10$, the y-intercept of the line $L$ is | Q | 7 |
| C | The line $y=-\frac{3 x}{4}+9$ crosses the $x$-axis at $P$ and the $y$-axis at $Q$. Point $T$ lies on $PQ$ and its coordinates are $( r , s )$. If $\frac{\text { Area of triangle } P O Q}{\text { Area of triangle TOP }}=3$, then the value of $(r+s)$ equals | R | 8 |
| D | Let $ABC$ be a triangle with $AB =3, BC =4$ and $AC =5$. Let $I$ be the centre of the circle inscribed in triangle $ABC$. The product of the distances of incentre from the vertices $A , B$ and $C$ of the triangle $ABC$, is | S | 10 |
| T | 11 | ||
Straight Lines
Solution: