Q. Area of the greatest rectangle that can be inscribed in the ellipse $\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1$ is :
AIEEEAIEEE 2005
Solution:
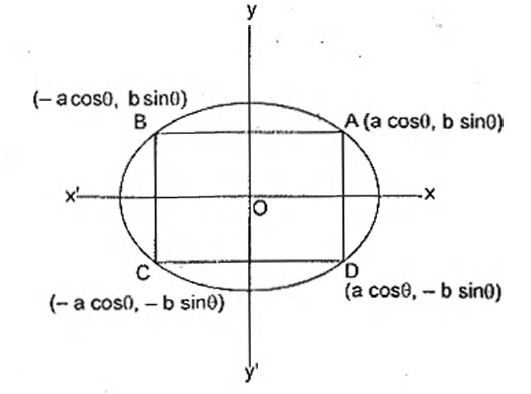
Key Idea : The parametric co-ordinates of point that lies on an ellipse $\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1 are \left(a\,cos\,0, b\, sin\, 0\right).$
Let the co-ordinates of the vertices of rectangle
$ABCD$ are $A \left(a\, cos \,0, b\, sin\, 0\right), B\left(-a\,cos\,0,\,b\,sin\,0\right) C\left(-a\,cos\,0,\,b\,sin\,0\right)$ and $D\left(a\,cos\,0,\,-b\,sin\,0\right)$ then
length of rectangle, $AB = 2a\, cos\, 0$
and breadth of rectangle, $AD =2b\, sin \,0$
\therefore Area of rectangle = AB\times AD
$= 2a\, cos\, 0 \times 26 \,sin\, 0$
$\Rightarrow $ Area of rectangle, $A = 2\,ab\, sin \,20\,...\left(i\right)$
$\therefore \frac{dA}{d\theta }=2\times2\,ab\,cos\,2\theta$
On putting $\frac{dA}{d0}=0$ for maxima or minima.
$\therefore \frac{dA}{d\theta }=0$
$\Rightarrow cos\,2\theta =0$
$\Rightarrow 2\theta=\frac{\pi}{2} \Rightarrow \theta =\frac{\pi}{4}$
Now $\frac{d^{2}A}{d\theta ^{2}}=-8ab\,sin^{2}\,\theta$
Now $\left(\frac{d^{2}A}{d\theta ^{2}}\right)_{_{\theta =\frac{\pi}{4}}} < 0$
$\therefore $ Area is maximum at $\theta =\frac{\pi }{4}$
$\Rightarrow $ Maximum Area of rectangle $= 2\,ab\,sq unit. \left(From \left(i\right)\right)$
Alternate Solution
From Eq. (i)
Area of rectangle, $A = 2\,ab\, sin\, 2\theta$
$\because A \,\propto\,sin\,2\theta$ and $-1 \le sin\,2\theta \le1$
$\therefore $ A is maximum when $sin\,2\theta=1$
$\Rightarrow $ Maximum area of rectangle $= 2ab\,sq\, unit.$