Q.
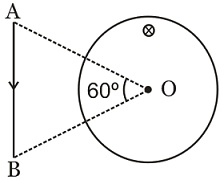
A very long cylindrical wire is carrying a current $I_{o}$ distributed uniformly over its cross-section area. $O$ is the centre of the cross-section of the wire and the direction of current in into the plane of the figure. The value of $\displaystyle \int _{A}^{B}\overset{ \rightarrow }{B}.\overset{ \rightarrow }{dI}$ along the path $AB$ (from $A$ to $B$ ) is
NTA AbhyasNTA Abhyas 2020Moving Charges and Magnetism
Solution: