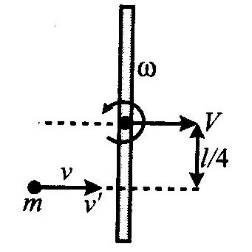
Q. A uniform smooth rod (mass $m$ and length $l$ ) placed on a smooth horizontal floor is hit by a particle (mass $m$ ) moving on the floor, at a distance $\frac{l}{4}$ from one end elastically ( $e=1$ ). The distance travelled by the centre of the rod after the collision, when it has completed three revolutions, will be
NTA AbhyasNTA Abhyas 2020System of Particles and Rotational Motion
Solution: