Q.
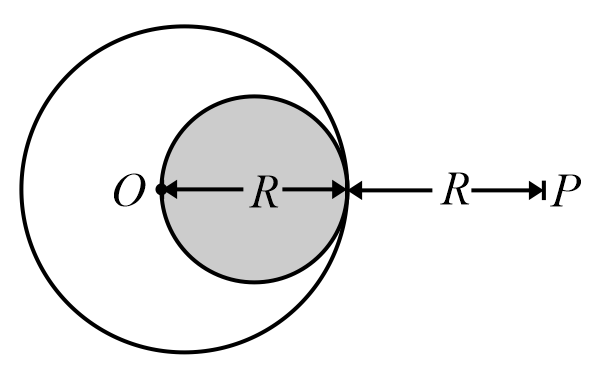
A solid sphere of uniform density and radius $r$ applies a gravitational force of attraction equal to $F_{1}$ on a particle placed at $P$ , at a distance $2R$ from the centre $O$ of the sphere. A spherical cavity of the radius $\frac{R}{2}$ is now made in the sphere as shown in the figure. The sphere with cavity now applies a gravitational force $F_{2}$ on the same particle placed at $P$ . The ratio $\frac{F_{2}}{F_{1}}$ will be,
NTA AbhyasNTA Abhyas 2022
Solution: