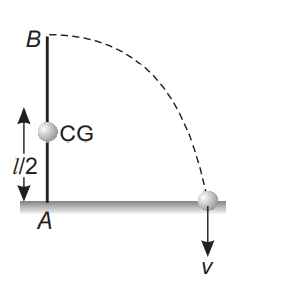
Q. A rod of length $l$ is held vertically stationary with its lower end located at a point $P$, on the horizontal plane. When the rod is released to topple about $P$, the velocity of the upper end of the rod with which it hits the ground is
VITEEEVITEEE 2009
Solution: