Q.
A horizontal oriented tube AB of length 5 $m$ rotates with a constant angular velocity $0.5 rad / s$ about a stationary vertical axis $OO$ ' passing through the end $A$. The tube is filled with ideal fluid. The end of the tube is open, the closed end $B$ has a very small orifice. The velocity with which the liquid comes out from the hole (in $m / s$ ) is: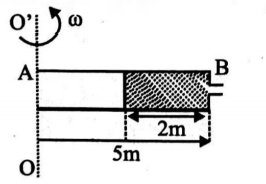
Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Solution: