- Tardigrade
- Question
- Chemistry
- Amino acids contain an - NH 2 as well as a - COOH group. In many non-polar solvents, they exist in its neutral form, but in aqueous solution, they exist as dipolar ions (Zwitter ions) <img class=img-fluid question-image alt=image src=https://cdn.tardigrade.in/img/question/chemistry/b752e834895155ebc8ff67ef14a8753e-.png /> This explains their several characteristics properties, like composition on heating, solubility in water, large dipole moment If the pH is lowered significantly, say to pH 1 or 2, then carboxylate ion will be protonated, likewise at a very high pH, the free amino group is exposed by deprotonation of ammonium ion <img class=img-fluid question-image alt=image src=https://cdn.tardigrade.in/img/question/chemistry/699a24096bb93ac92d4abd59aa5ae3e5-.png /> There is a pH corresponding to each amino acid where it remains neutral and neither moves towards cathode nor anode when the electric field is applied. This pH of the solution is referred to as isoelectric point. For example, the isoelectric point of alanine is 6.01, that of isoleucine is 6.02 and so on Hence, the ionic form of the amino carboxylic group is the effect of pH on the functional group in the side chain of amino acid. The side chain of many amino acids contain a functional group that can also be protonated or deprotonated For the thiol group of cysteine at pH 8.2, of p Ka is 8.3, the concentration ratio of R S - v S R S H <img class=img-fluid question-image alt=image src=https://cdn.tardigrade.in/img/question/chemistry/b60dd91b92cc1af463acf347a7631fb0-.png />
Q.
Amino acids contain an as well as a group. In many non-polar solvents, they exist in its neutral form, but in aqueous solution, they exist as dipolar ions (Zwitter ions)
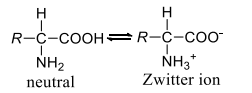
This explains their several characteristics properties, like composition on heating, solubility in water, large dipole moment
If the is lowered significantly, say to or 2, then carboxylate ion will be protonated, likewise at a very high pH, the free amino group is exposed by deprotonation of ammonium ion
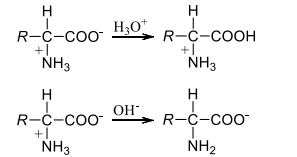
There is a pH corresponding to each amino acid where it remains neutral and neither moves towards cathode nor anode when the electric field is applied. This of the solution is referred to as isoelectric point. For example, the isoelectric point of alanine is , that of isoleucine is and so on
Hence, the ionic form of the amino carboxylic group is the effect of on the functional group in the side chain of amino acid. The side chain of many amino acids contain a functional group that can also be protonated or deprotonated
For the thiol group of cysteine at pH , of is , the concentration ratio of
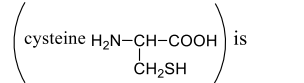
Solution: